Methodology
Earthquakes
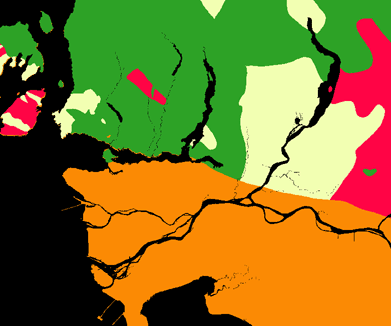
For both earthquakes and landslides, faults were reclassed to values of 1 for faults and the remainder as 0. DISTANCE was applied to obtain the distance from the fault lines.
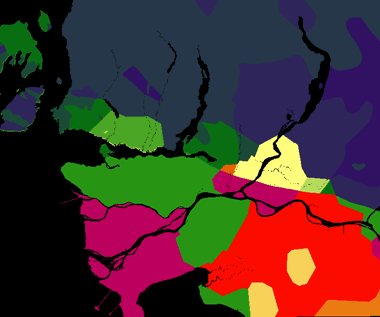
For soil stability and liquefication potential, the bedrock age was arranged from oldest to youngest and grouped into 4 categories with group 1 as the oldest, and group 4 as the youngest group. They were group in the following manner:
| 1 | Lower Jurassic to Middle Jurassic |
| 2 | Late Jurassic Late Jurassic to Early Cretaceous Mesozoic |
| 3 | Lower Cretaceous |
| 4 | Oligocene Eocene |
The surficial data raster was reclassified to assign values for succeptibility to liquefication. They were assigned values from 1 to 7 with 1 being the most succeptible and 7 being the most resistant. They were arranged with the order:
| 1 | Ra - alpine complexes (rock, colluvium and till) |
| 2 | Tv - till veneer (thin and discontinuous till) |
| 3 | cM - coarse grained glacio / marine sand and gravel |
| 4 | rC - colluvial rubble and silt |
| 5 | Gp - glacialfluvial plain (sand and gravel deposits) |
| 6 | Mv - glacial lag and marine deposits (sand, gravel and pockets of finer sediments) |
| 7 | A - alluvial deposits (stratified silt, sand, clay and gravel) |
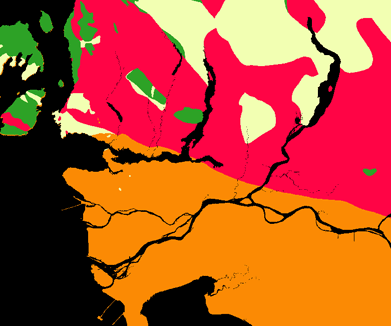
The reclassed surficial and bedrock data was then overlaid together with multiplication as the operation to determine levels of risk based on these 2 factors.
Landslides
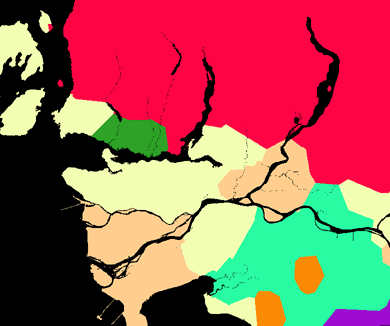
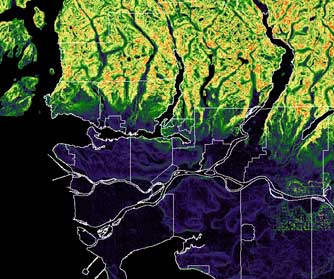
The SLOPES operation was applied to the GVRD 50m DEM to determine the angle of slopes.
Distance from water sources was obtained by applying the DISTANCE function to water sources raster.
The bedrock type was reclassed into four groups based on resistance to weathering which can lead to reduced cohesive strength and eventually cause landslides. A higher number indicated a higher succeptibility to weathering. The bedrock type was reclassed in the following order:
| 1 | metamorphic rock undivided basaltic volcanic rocks |
| 2 | quartz dioritic intrusive rock dioritic to gabbroic intrusive rock grandioritic intrusive rocks |
| 3 | argillite, greywacke, wacke, conglomerate marine sedimentary and volcanic rock |
| 4 | undivided sedimentary rock |
The raster for distance from fault lines created in the earthquake section was also used to determine risk of landslides.
Flooding
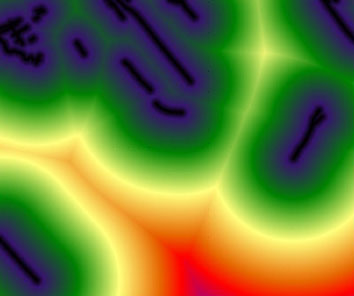
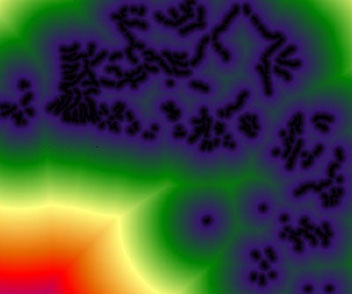
FUZZY was applied to the GVRD DEM to determine areas most likely subject to flooding. An arbitrary value of 1m above sea level was used as a height water may rise up to.
FUZZY settings for determining areas at risk of flooding due to 1m rise of water above sea level