| Home |
Study
Design and Hypothesis |
Research
Background |
Data Sources |
| Methodology |
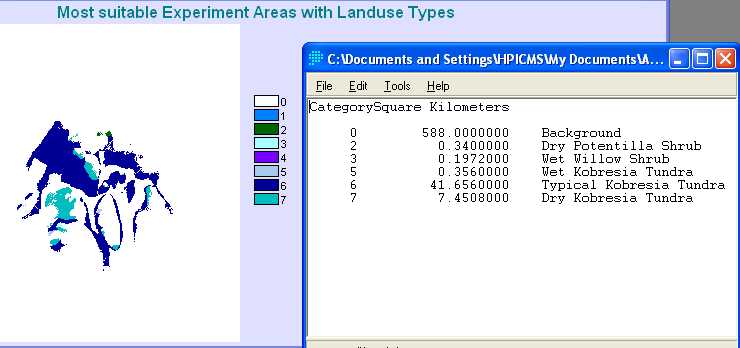
Spatial
Analysis |
Conclusion |
Problems
and Discussion |
| Power of
IDW |
2 |
3 |
4 |
| Neighbor
Cell Number 8 |
0.64 |
1.86 |
2.65 |
| Neighbor
Cell Number 16 |
1.32 |
2.49 |
3.17 |
| Neighbor
Cell Number 24 |
1.20 |
2.43 |
3.16 |

 Previous
Home
Next
Previous
Home
Next