Home Study Area
Data Collection Methodology Spatial
Analysis Methodological & Operational Problems
Methodology
OBJECTIVE: The goal of the project was to gather data
on land use in
CRITERIA:
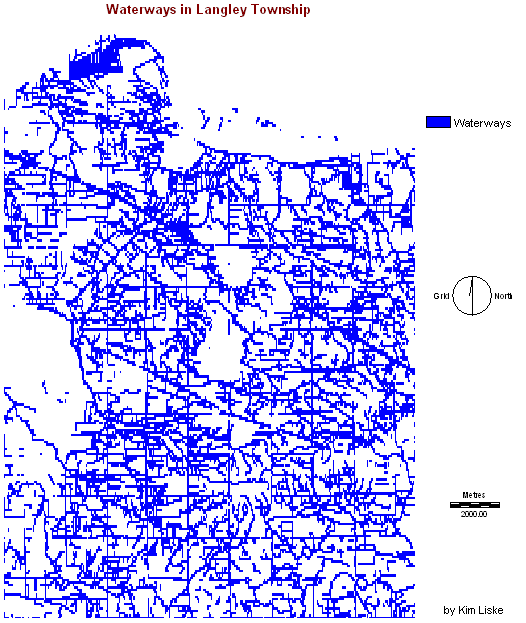
1. Protected
areas surrounding
waterways
1
.2.
Waterways were made a
Boolean constraint where urbanization was not permitted within the buffered
area.
2.
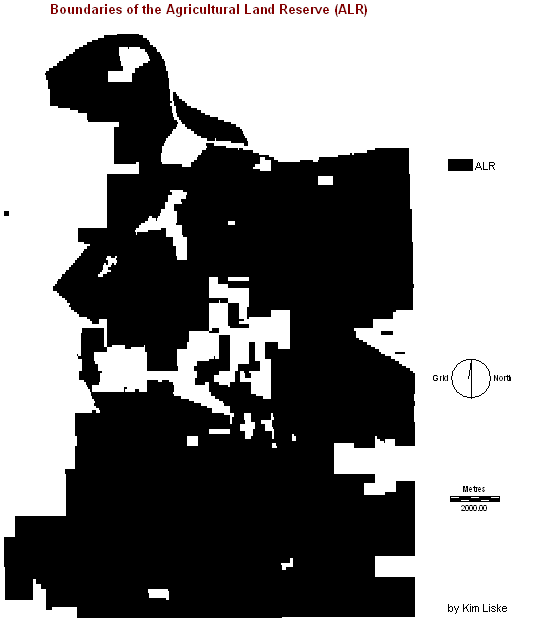
Protected areas in the Agricultural Land Reserve (ALR) 2.1.
Areas
included in the ALR were ruled out completely since they are not available
for major development. 2.2.
The
ALR was made a Boolean constraint where urbanization was not permitted within
the ALR Boundary.
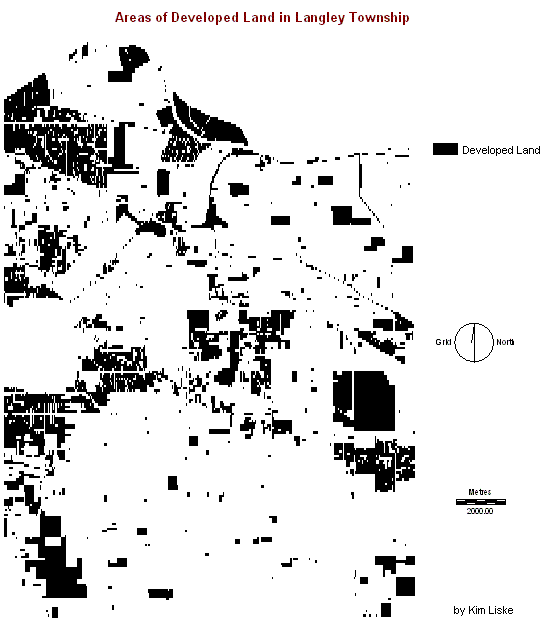
3.
Areas already designated as high density residential, commercial, or
industrial
3.1. Areas that are already well developed
will not be used for construction of high density communities. Residential areas that feature large lots
with single residences may be developed since the lots may be sold and
developed (ex.
3.2. Areas that are already well
developed were made a Boolean constraint where urbanization was not
permitted within the developed areas.
4.
Proximity to developed areas 4.1. Residential construction was considered to be likely close
to areas that were already developed and thus already had services in place
(ex. Shopping, activities, etc;)
4.2. Proximity to
developed areas was weighted and used in the MCE WLC analysis.
This layer was created by reclassifying the landuse layer into a boolean
map where high density residential, commercial, industrial, transportation,
communication, utility, civic, institutional, and recreational.
5.
Accessibility to roads 5.1. Proximity
to major and minor roads were weighted and used
in the Multi Criteria
Evaluation (MCE) Weighted Linear Combination (WLC)
analysis. 5.2.
The layer shown was further broken into major and minor
roads prior to the WLC analysis. Details
on this can be seen in the The layer shown was
created by reclassifying the roads according to
make every road category
into one object.
6.
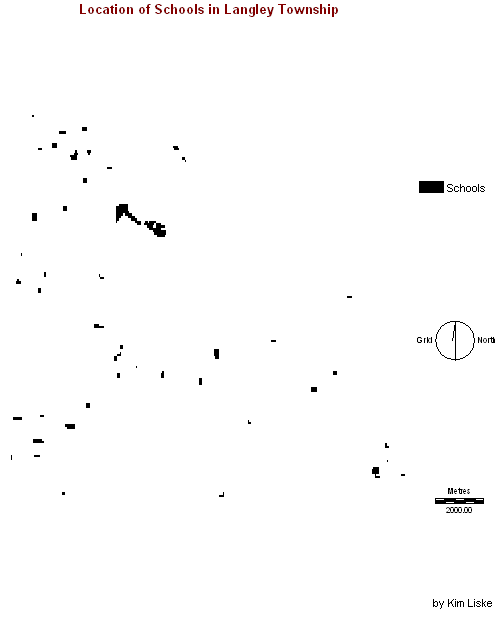
Proximity to schools
6.1.
This factor is only
somewhat important. Once a community
starts to be developed schools are usually built to accommodate the
new population.
The area then grows rapidly as families choose to buy close to a
school. New schools are also a
population draw. This is true of
primary, secondary, and post-secondary institutions.
6.2. Proximity to
schools was weighted and used in the MCE WLC analysis.
The layer shown was created by querying the parcels table in ArcView for
parcels of actual use code 650 (schools) and deleting all othe the other
records. Once imported into Idrisi, the layer was reclassed into a
Boolean layer showing only the locations of schools within