Earthquake Hazard GIS Modelling in the Greater Vancouver Regional District
Spatial Analysis
The Multi-critieria (MCE) Weighted-linear combination (WLC) analysis is used in modelling the relative earthquake hazards based on the four geotechnical hazards and one constraint:
- Standardized Soil Amplification Map (Factor)
- Standardized Soil Liquefaction (Factor)
- Slope Instability (Factor)
- Earthquake Intensity (Factor)
- within GVRD municipality extent (Constraint)
The relative weights of the four factors are shown in the following constructed pairwise comparison matrix. As shown, I've assigned soil liquefaction be the most important factor, same weight on slope instability & amplification and least import for earthquake intensity.
| liquefactionstand | amplificationstand | slopeinstability | earthquakeintensity | |
| liquefactionstand | 1 | |||
| amplificationstand | 1/2 | 1 | ||
| slopeinstability | 1/2 | 1 | 1 | |
| earthquakeintensity | 1/4 | 1/2 | 1/2 | 1 |
These values were input into the weighted module and the resulted eigenvector of weights was :
liqueficationstand : 0.4444
amplificationstand : 0.2222
slopeinstability : 0.2222
earthquakeintensity : 0.1111
Consistency ratio = 0.00
Consistency is acceptable.
The above weight factors are saved as eqhazard.pdf and this file is used in the weighted-linear module of the multi-criteria analysis for deriving the relative earthquake hazard map. The following shows the cartographic model for the above steps:
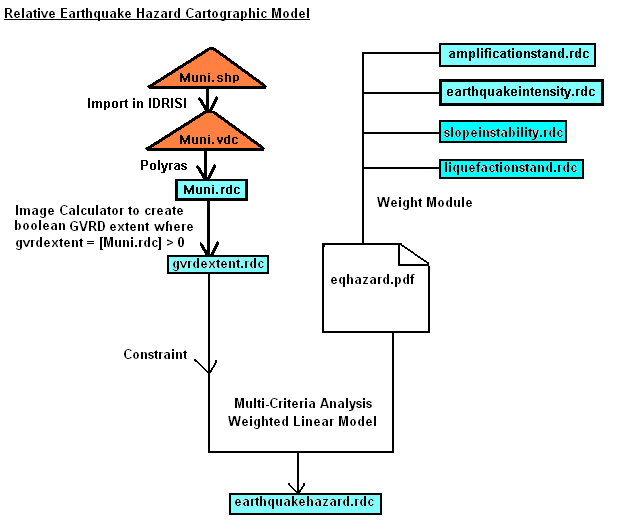 |
The resulted Relative Earthquake Hazard Map of GVRD (earthquakehazrd.rdc) is shown in the next section Results.
NOTE: This web is created on Nov 19, 2002 by Carol Cheuk (Student #: 973003525) for course GEOG355 Project. It is optimized for resolutions of 1024x768 and above and requires the use of Microsoft Internet Explorer or Javascript enable browser for best results.