After the data manipulated using ArcMap, all the data files which were then in ASCII format was imported into Idrisi. In IDRISI, in order to compare images by performing functions on them, all the images being used in the analysis have to in the same file and data type as well as it has to contain the same number of rows and columns. In order to accomplish this, the Land-use file was used as a reference image. All the files were converted into byte data type and Binary file type. Then utilizing the RESAMPLE function and the Land-use file as the reference image, the files that did not contain the same number of cells as the land-use images was resampled. This resulted in all images being in a 20 metre by 20 metres resolution with the same data and file type and with the same number of rows and columns. This Resample function had to be performed on the sky-train file, the bus-routes, streets, shopping malls as well as the libraries file. Below is an example (Image 1) of how the resampling occurred for all the libraries within the GVRD using Ground Control Points.
*Note: You can enlarge each image by clicking on it.
Since the method of analysis is Multi-Criteria Evaluation for this project, the factors and constraints being considered have to be distinguished. For this project there are 6 factors that are considered for the study. Factors represent attributes that one would consider significant in determining the ideal location. For this project the factors are on a continuous scale of probability as is desired in non-Boolean standardization where suitability ranges from 0 to 255. The factors that were considered include (you may click on the desired factor to go the correct section):
|
Distance to Bus Stations |
Distance to Skytrain lines |
Proximity of Shopping centres/malls |
Proximity of Libraries |
The residential type |
In addition to factors there are two constraints affecting the study area. Constraints are basically limits that we put on our study region, it represents areas that is not considered or considered in the form of Boolean images. The two constraints are (you may click on the constraints to go the desired section):
Possible Residences |
Roads |
To distinguish the desired area of study, the GVRD land-use file was imported into IDRISI to display the entire region of the GVRD. This map was reclassed in IDRISI to display the cities and villages within the GVRD (Image 2).
Image 3 Image 4
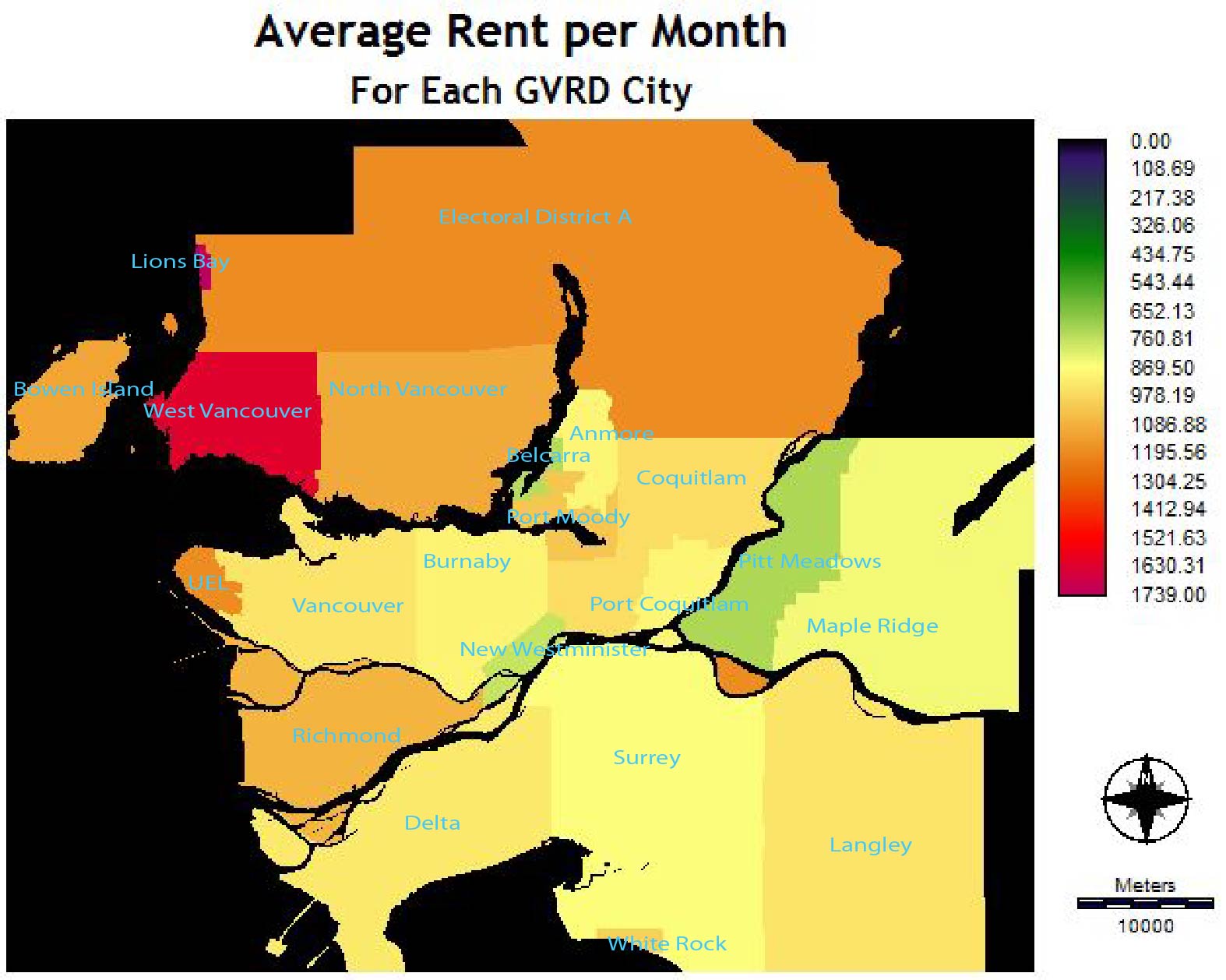
Using ArcMap the average rent for each city per month was determined. Then the area of study cities image was reclassed to display the average rent value of each city as is displayed in the Average Rent per Month image (Image 3). With the Decision Wizard the FUZZY Module was used to conduct the non-Boolean standardization. For this particular factor as rent decreases, the level of suitability should increase (Image 5). Thus the following specifics were utilized and the result is displayed above (Image 4):
Image 5
Image 6 Image 7
Image 8
After importing the bus routes image into IDRISI, the Boolean image had to be resampled to match the data type, file type and number of rows and columns of the other images. In order to conduct this operation, the RESAMPLE function was utilized with the land-use image as the reference image following the process as displayed in Image 1in this Methodology page. The result is displayed above (Image 6). Then using the DISTANCE function, the distance from roads to all other regions in the study area was calculated (Image 7). This Distance image was used in the Decision Wizard with the FUZZY module for non-Boolean standardization. New residents would want to in a region that is in close proximity to Bus routes, thus the further the distance from the available bus routes the lower the level of suitability should be. Using Google maps direction function for walking it was determined that it takes approximately 10 minutes to walk a 1000 metres. With this information it was determined that the level of suitability would be highest for regions that are within 1000 metres of a bus route. Also it was determined that new residents would not even consider living in an area from which you would have to walk more than 3500 metres for bus service. Thus, 0 to 1000 metres was assigned the highest suitability and then the level of suitability decreased at a continuous scale until 3500 metres. Any distance beyond that point was not considered. The image below (Image 9) represents the specific standardization format that was chosen for this particular factor. The results of the function is displayed in above (Image 8).
Image 9
Image 10 Image 11
Image 12
The Sky-train routes image was imported into IDRISI resulting a Boolean image; it displayed regions where there was no sky-train routes and regions where there was. This Boolean image was also resampled to match the data type, file type and number of rows and columns of the other images. This process was implemented using the RESAMPLE function. With the RESAMPLE function, the land-use image was used as a reference to get the most accurate approximation of the desired region. The result of this function is displayed above (Image 10). In addition as similar to the Distance to Bus-routes factor, using the DISTANCE module, the distance from sky-train routes to all other regions in the study area was calculated (Image 11). Using the FUZZY module in the Discussion Wizard, non-Boolean standardization was applied to the Distance image of Sky-train routes. New immigrants would desire to live in close approximation to sky-train routes for easy access to neighbouring cities for job opportunities and other requirements. Again, using Google maps’ direction function for transit it was determined that one can take a bus to a sky-train station and travel further from there. With this information it was determined that the level of suitability would be highest for regions that are within 12500 metres of a bus route. Also it was determined that new residents would not even consider living in an area from which you would have to walk and travel on bus for more than 18750 metres for sky-train service. Thus, 0 to 12500 metres was assigned the highest suitability and then the level of suitability decreased at a continuous scale until 18750 metres. Any distance beyond that point was not considered. The image below (Image 13) represents the specific standardization format that was chosen for this particular factor. The results of the function is displayed in above (Image 12).
Image 13
Image 14 Image 15
Image 16
Proximity to shopping centres and malls was determined by initially using the RESAMPLE module to resample the locations of the malls with the land-use image as a reference and the result in displayed above (Image 14). Using the DISTANCE module, the distance from these centres was calculated (Image 15). Finally the distance image was standardized using the FUZZY module to determine a level of suitability between 0 and 255(Image 16). As distance increases the suitability value should decrease thus the following standardization format was used (Image 17).
Similar to the proximity to shopping centres image, the proximity to libraries image was also Resampled (Image 18). The DISTANCE module was utilized to calculate the distance from the libraries to anywhere else in the study area(Image 19).The distance was standardized using the FUZZY module and with the assumption that as distance increases the level of suitability decreases(Image 20). The format for standardization is represented below (Image 21).
| Residential (Housing) Type | Suitability Score |
| Single Family Homes | 255 |
| Townhouse and low-rise apartments | 225 |
| Commercial-Residential Mixed | 100 |
| High-rise Appartments | 75 |
| Remaining Area | 0 |
As mentioned in the Background section, new immigrants who commonly move into the GVRD with families would prefer to live in a certain type of residence. Thus using the RECLASS module, the land-use image of the GVRD was reclassed into five different values. As seen in the table above, single family homes were assigned a value of 255 representing the most desired type of residence. Town-house and low-rise apartments were slightly less at 225 due it being less suitable to live with a family. Commercial area were assigned a value of 100 because living between commercial areas can serve to be loud and hard. High-rise apartments were given a value of 75 because they are not suitable for families with children and they are commonly high in rent value. The remaining region was assigned a value of 0. For this factor, since standardization was manually done, the FUZZY module was not utilized. The image below represents the reclassed image of the residential types (Image 22).
There are two constraints utilized in this study. This includes the residential constraint and the roads/streets constraint. The residential constraint is chosen because for the study only the regions where residential living is possible needs to be considered (Image 23). The remaining areas are not of use for the study. For this, a Boolean image was developed by using the RECLASS module to assign all possible areas for residential living a value of 1 and the remaining area was given a value of 0. The roads/streets constraint is used because, residences should be within a certain distance from existing roads. If not, it would be difficult for travel. Thus using the Boolean image of the roads in the study region a buffer was created by using the BUFFER module. This process created a buffer of 50 metres around the roads representing the area where residential living is possible (Image 24).