Power, ![]() , Sample Size
, Sample Size
STAT 330 Lecture 15
Reading for Today's Lecture: 6.2, 8.1, 8.2
Goals of Today's Lecture:
Today's notes
Power, ![]() , Sample Size
, Sample Size
Definition: the power function of a hypothesis test procedure is
![]()
Recall: Type I error is incorrect rejection. Type 2 error is incorrect acceptance.
Definition: The level of a test is the largest probability of rejection for
![]() in the null hypothesis:
in the null hypothesis:
![]()
Typically if the null hypothesis is like ![]() the value of
the value of ![]() is actually
is actually ![]() , that is, the edge of the null hypothesis gives the
highest risk of incorrect rejection.
, that is, the edge of the null hypothesis gives the
highest risk of incorrect rejection.
Definition: The probability of a type two error is a function ![]() defined for
defined for ![]() by
by
![]()
Thus
![]()
for ![]() not in the Null.
not in the Null.
A good test procedure has
Example 1: ![]() iid
iid ![]() . {WE PRETEND
. {WE PRETEND
![]() IS KNOWN.) To test
IS KNOWN.) To test ![]() vs
vs ![]() at level
at level ![]() : reject if
: reject if
![]()
Now
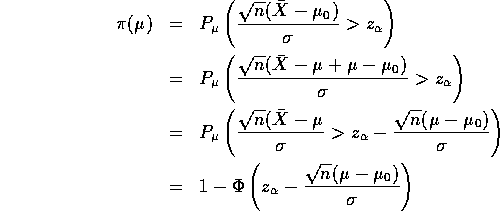
which is the area to the right of
![]()
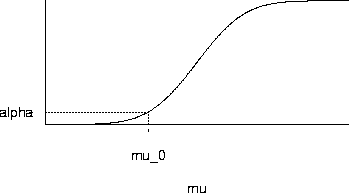
under the standard normal curve. Here is a graph of the power function:
Power and Sample Size Determination
Scenarios:
Catalyst example: ![]() will be yields for new (catalyzed)
method. Assume old method had:
will be yields for new (catalyzed)
method. Assume old method had:
We will test ![]() against
against ![]() at level
at level ![]() and reject if
and reject if
![]()
How big should n be? To answer we need to more ingredients:
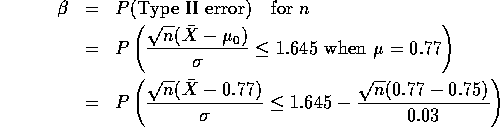
which is the area to the left of
![]()
But the area is 10% when
![]()
so that the general formula is
![]()
or, solving
![]()
or
![]()
In our example
|
| | |
|
| | |
|
| | |
so that
![]()
We round up to n=20 to get the type II error rate to be definitely under 10%.