Methodology
A multi-criteria evaluation was used to determine levels of fire hazard around Metro Vancouver. This type of evaluation uses two types of criteria: constraints and factors. Constraints limit areas from consideration, while factors affect the level of suitability of an area. Two constraints and six factors were used in this MCE.
Constraints
The two constraints used in this MCE were:
- Study area - Only areas in Metro Vancouver are being evaluated for this project
- Water bodies - Water bodies are not flammable, and do not represent fire hazard
Factors
The six factors used in this MCE were:
- Aspect - South-facing slopes receive more sun exposure, and are therefore drier and more susceptible to burning.
- Slope - The steeper the slope, the more easily fire will spread, due to a variety of causes, including the upward movement of air caused by the heat of the fire, and way fire spreads upwards, using fuel at progressively higher heights to spread
- Land use - Different types of vegetation cover, building materials, and activities present different levels of fire hazard
- Road distance - Accessibility reduces fire hazard, as it allows emergency services to respond to a fire
- Fire hall distance - Being closer to a fire hall improves response time
- Water distance - Water bodies act as a natural barrier to fire, and can be used as a source to extinguish fires
Of these six factor, land use is the only one that had values explicitly defined. Each land use type was given a fire hazard value based on generalized assumptions of the buildings, land cover, and activites taking place on land classified as that type. This put water as the obvious lowest risk, and extractive industries at the highest risk, with everything else falling somewhere in between. The complete list of values can be found below.
| Land use | Hazard rating (0-255) |
|---|---|
| Lakes and Water Bodies | 0 |
| Open and Undeveloped | 25 |
| Recreation and Protected Natural Areas | 200 |
| Protected Watershed | 50 |
| Transportation, Communication and Utilities | 50 |
| Residential - Rural | 100 |
| Residential - Single Family | 100 |
| Industrial - Extractive | 255 |
| Institutional | 50 |
| Commercial | 125 |
| Residential - Townhouse and Low-rise Apart | 125 |
| Industrial | 225 |
| Harvesting and Research | 75 |
| Commercial - Residential/Mixed | 150 |
| Residential - High-rise Apartments | 50 |
| Agricultural | 75 |
The other five factors were scaled between the values 0 and 255 using the FUZZY module. The function shapes and control points are listed below.
| Input file | Membership function type | Membership function shape | Control points | Output fuzzy file |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| aspect | Sigmoidal | Symmetric | a: 0.0 b: 180.0 c: 180.0 d: 360.0 |
aspectfuzz |
| slope | J-shaped | Monotonically increasing | a: 0.0 b: 74.3692 |
slopefuzz |
| roaddist | Linear | Monotonically increasing | a: 0.0 b: 24406.80 |
roadfuzz |
| waterdist | J-shaped | Monotonically increasing | a: 0.0 b: 23983.0 |
waterfuzz |
| firehalldist | Linear | Monotonically increasing | a: 0.0 b: 41063.3 |
firehallfuzz |
Factor weights
The factor weights were derived using the AHP weight derivation, which performs pairwise comparisons of weights to determine factor weights that sum to 1. The values used and resultant factors are shown below.
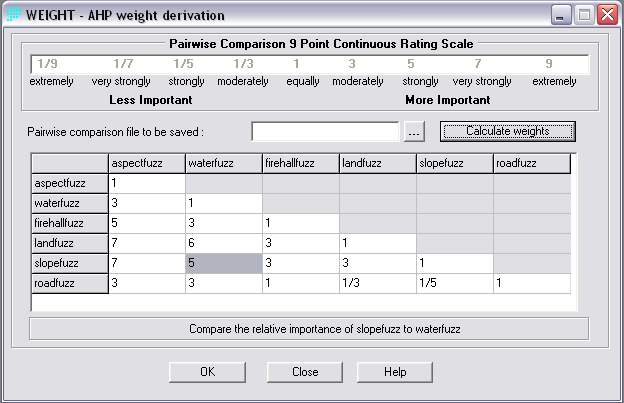
The eigenvector of weights is :
aspectfuzz : 0.0331
waterfuzz : 0.0569
firehallfuzz : 0.1253
landfuzz : 0.2636
slopefuzz : 0.4150
roadfuzz : 0.1061
Consistency ratio = 0.05
Consistency is acceptable.
Cartographic model
The cartographic model of analysis performed prior to using the MCE Decision Wizard is shown below.
