Ranked No.1 for Newest Technologies in 5G
As the 5G technology market comes into focus, we’re seeing a number of technologies emerge as vital to the 5G experience.
As the 5G technology market comes into focus, we’re seeing a number of technologies emerge as vital to the 5G experience.
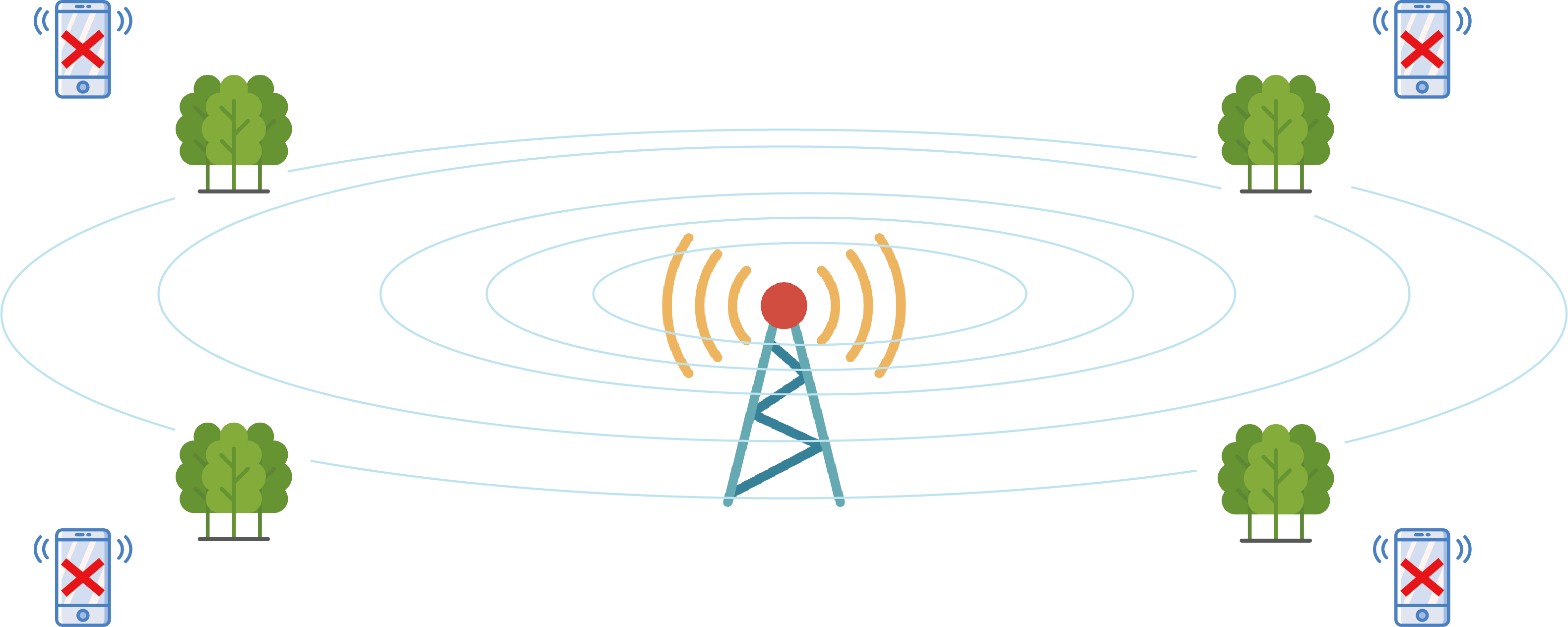
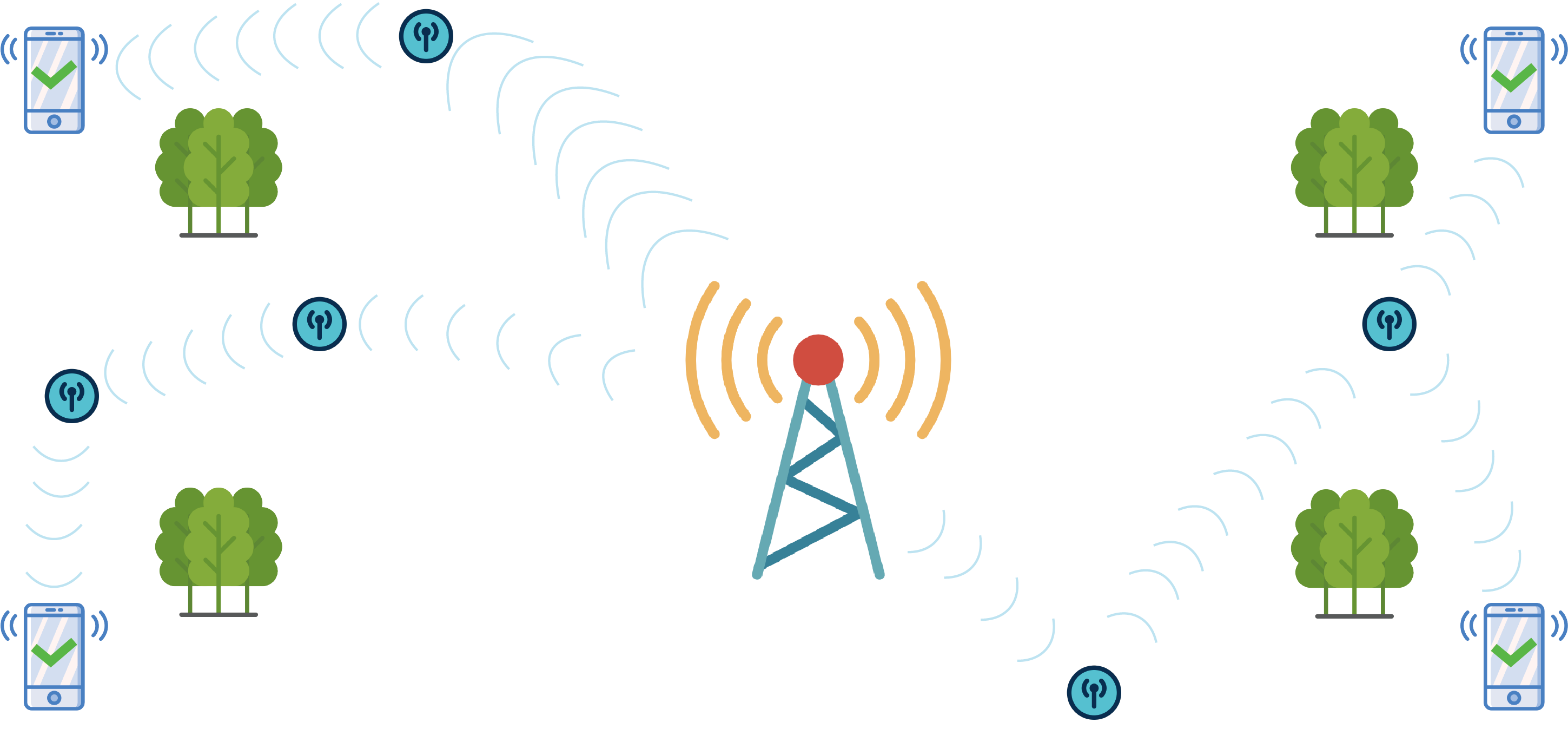
Your smart phone and other electronic devices in your home, use very specific frequencies on the radio frequency spectrum. Typically, those under 6GHz, but these frequencies are starting to get more crowded. Carriers can only squeeze so many bits of data on the same amount of radio frequency spectrum. As more devices come online, we're going to start to see lower service and more dropped connections. The solution is to open up some new real estate. The researchers are experimenting with broadcasting on shorter millimeter waves, those that fall between 30 and 300 GHz. This section of spectrum has never been used before for mobile devices, and opening it up means more bandwidth for everyone.

Today’s wireless networks rely on large high powered cell towers to broadcast their signals over long distances, but remember higher frequency millimeter waves have a hard time traveling through obstacles which means if you move behind one, you lose your signal. Small cell networks would solve that problem, using thousands of low-power mini base stations, these base stations would be much closer together than traditional towers forming a sort of relay team to transmit signals around obstacles. This would be especially useful in cities as the user moved behind an obstacle his smartphone would automatically switch to a new base station in better range of his device, allowing him to keep his connection.
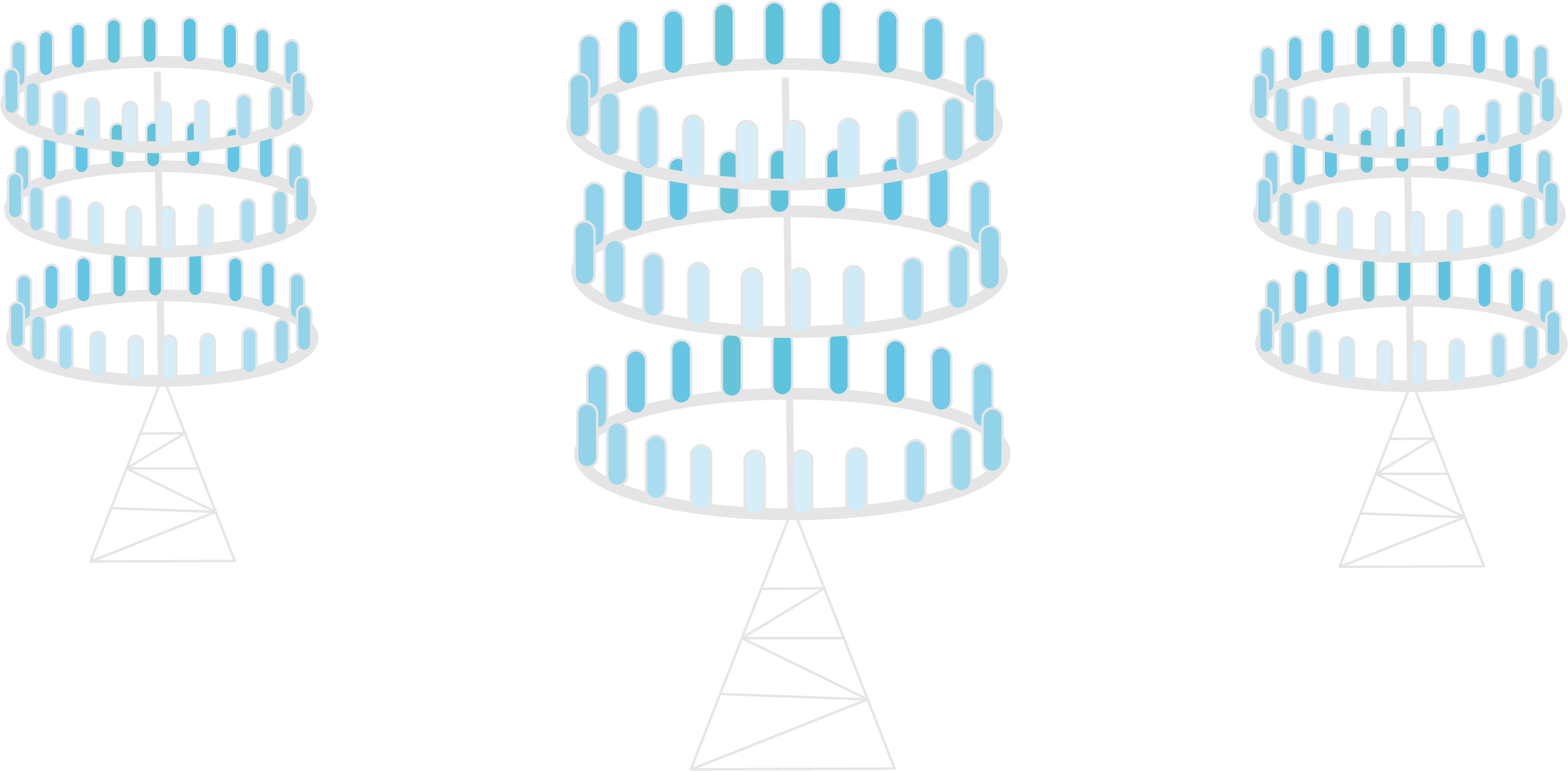
MIMO stands for multiple-input multiple-output. Today’s 4G base stations have about a dozen ports for antennas that handle all cellular traffic, but massive MIMO base stations can support a hundred ports, this could increase the capacity of today’s networks by ab factor of 22 or more, and massive MIMO comes with its own complications. Today’s cellular antennas broadcast information in every direction at once, and all of those crossing signals could cause serious interference.
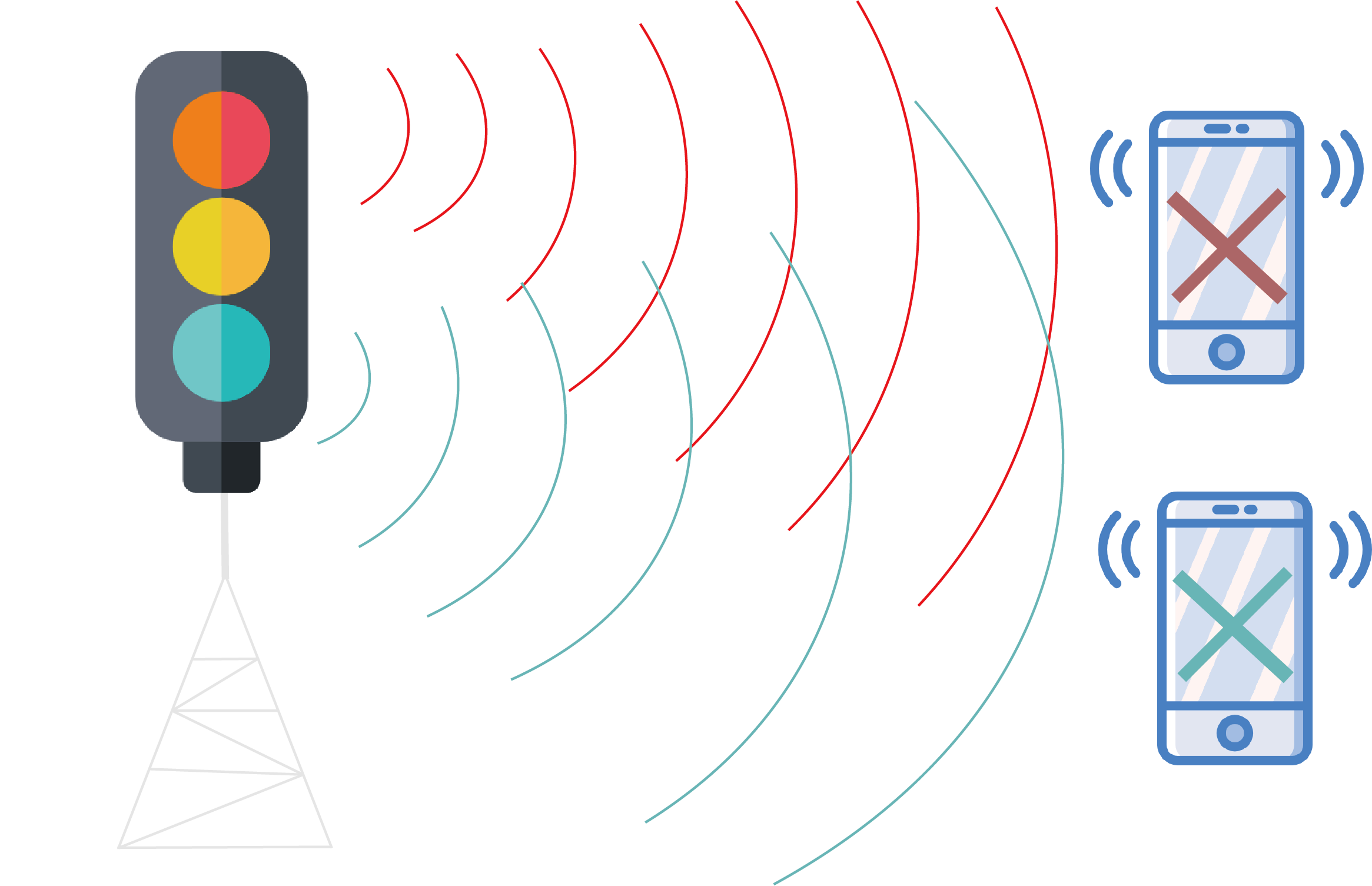

Here is an example of how beamforming works: image that you are in a cluster of buildings and you are trying to make a phone call, and your signal is ricocheting off of surrounding buildings and cries-crossing with other signals from users in the area. A massive MIMO base station receives all of these signals and keeps track of the timing and the direction of their arrival, the uses signal processing algorithms to triangulate exactly where each signal is coming from and plots the best transmission route back through the air to each phone. Sometimes, it will bounce individual packets of data in different directions off of buildings or other objects to keep signals from interfering with each other, and the result is a coherent data stream sent only to you.
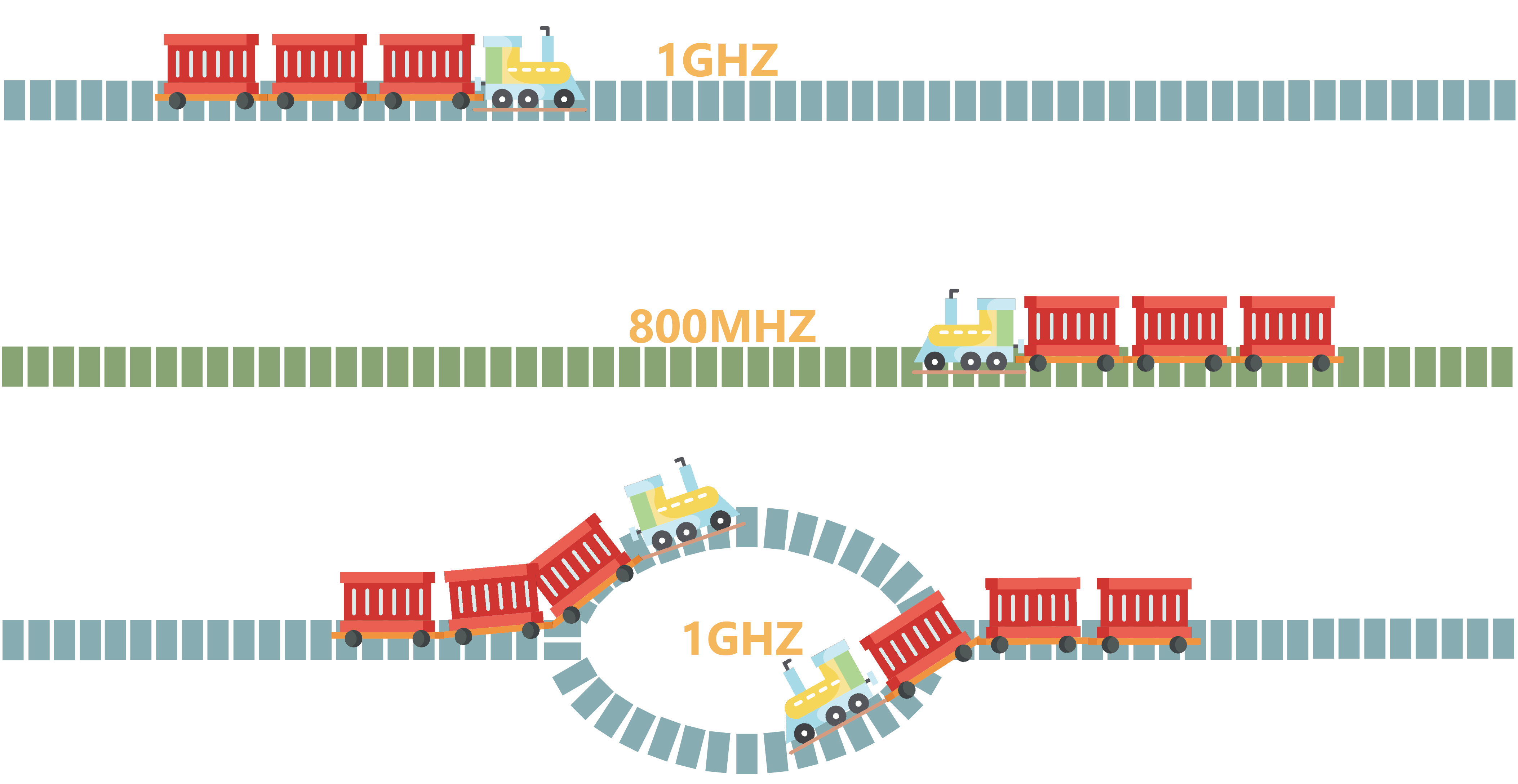
Today’s cellular base stations have exact same hold up a basic antenna can only do one job at a time, either transmit or receive. This is because of a principle called reciprocity which is the tendency for radio waves to travel both forward and backward along the same frequency. To understand this, it helps to think of a wave like a train loaded up with data: the frequency it’s traveling on is like the train track, and if there is a second train trying to go in the opposite direction on the same track, people need to get some interference. Up until now, the solution has been to have the trains take turns or to put all the trains on different tracks or frequencies, but people can make things more efficient by working around reciprocity. Researchers have used silicon transistors to create high speed switches that halt the backward of these waves, and it is kind of signaling system that can momentarily reroute to train so they can get pass each other, that means there is more getting done on each track a whole lot faster.
A Standard Essential Patent (SEP) is a patent that claims an invention that must be used to comply with a technical standard.
Source: WISPRO Technology Consulting Corporation
Companies with many SEPs can earn significant royalties and make their base stations, smartphones and other devices more competitively priced. In addition, countries with many 5G patents will be able to build advanced communication networks at lower cost and promote the growth of related industries.