&ndsp;
About the Vancouver Food Scrap Recycling Program
Metro Vancouver and member municipalities encourage food scraps recycling because it's the right thing to do, it takes waste out of our landfills, it reduces our methane contributions, and it creates compost and bioenergy.
Why are food scraps in garbage a problem?
When food and other organic materials end up in the garbage they:
- Create methane, a powerful greenhouse gas that adds to global warming. In the landfill, buried under layers of waste and without access to oxygen, food can't decompose properly.
- Use up a lot of precious landfill space. Space is limited, and creating more landfills is undesirable. Over 30% of what we send to the landfill in our region is compostable organics.
- Make waste-to-energy processes less efficient because of their high moisture content. About a third of the region's waste is disposed in the waste-to-energy facility.
What can be recycled in the Food Scraps Bin?
Food scraps need to be separated from regular garbage and placed into a green Food Scraps Recycling bin.


-
Fruit
Whole fruits, peels and rinds, seeds, citrus -
Vegetables
Whole vegetables, greens, seeds -
Dairy & Eggs
Milk, cheese, eggshells, baked goods -
Seafood
Fish, shellfish, shrimp -
Meats
Raw or cooked meat, bones, marrow -
Tea bags & Coffee Filters
Disposable tea bags, paper filters, coffee grounds, tea leaves -
Plants
Flowers, plants, branches, soil, seeds -
Soiled Paper & Cardboard
Used paper towels, pizza boxes, paper plates, wooden chopsticks
Check with your hauler to ensure you are recycling all that you can.
What cannot be recycled in the Food Scraps Bin?
This disposal ban is enforced the same as the region's other disposal bans. Waste is inspected when it is delivered to a regional disposal facility. If a waste load contains excessive amounts of recyclable materials, the hauler pays a surcharge of 50% on the cost of disposal.

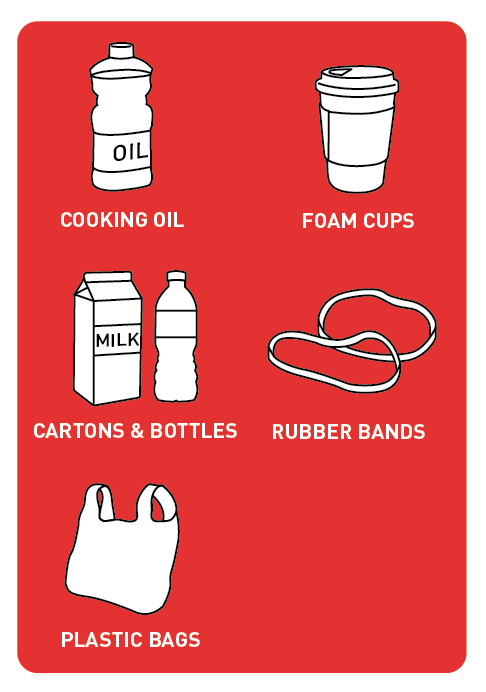
-
Foam
Foam coffee cups, foam containers, styrofoam packaging -
Cartons & Bottles
Milk cartons, juice cartons, plastic bottles -
Oil
Cooking oil, motor oil, body oils -
Plastic & Rubber
Plastic bags, twist-ties, rubber bands, bread clips