Abstract
LoRaWAN (Long Range Wireless Area Network) is a wireless communication protocol that makes use of the unlicensed spectrum. It is optimized for low-power and long-range applications as its name suggests, implementing 2 different types of nodes, gateways and end devices which are capable of communicating using a signal that sweeps multiple frequencies as it travels in time, also known as chirp. A chirp is capable of encoding information while providing resiliency to interference and therefore a long range. This study leverages ns-3 to implement a mechanism to simulate scenarios where the chirp characteristics are not fixed, just like in real-life deployed gateways and end devices, where the chirp characteristics change on a regular basis. To achieve this, a LoRaWAN module/IC (RYLR896: SX1276 chip with antenna) was selected to be modeled in the ns-3 simulation. As a result, the behavior of LoRa products that make use of that specific LoRa module can be more accurately simulated on ns-3.
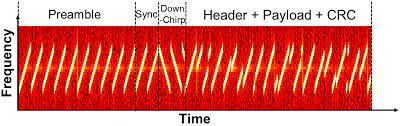
LoRa packet structure [8]
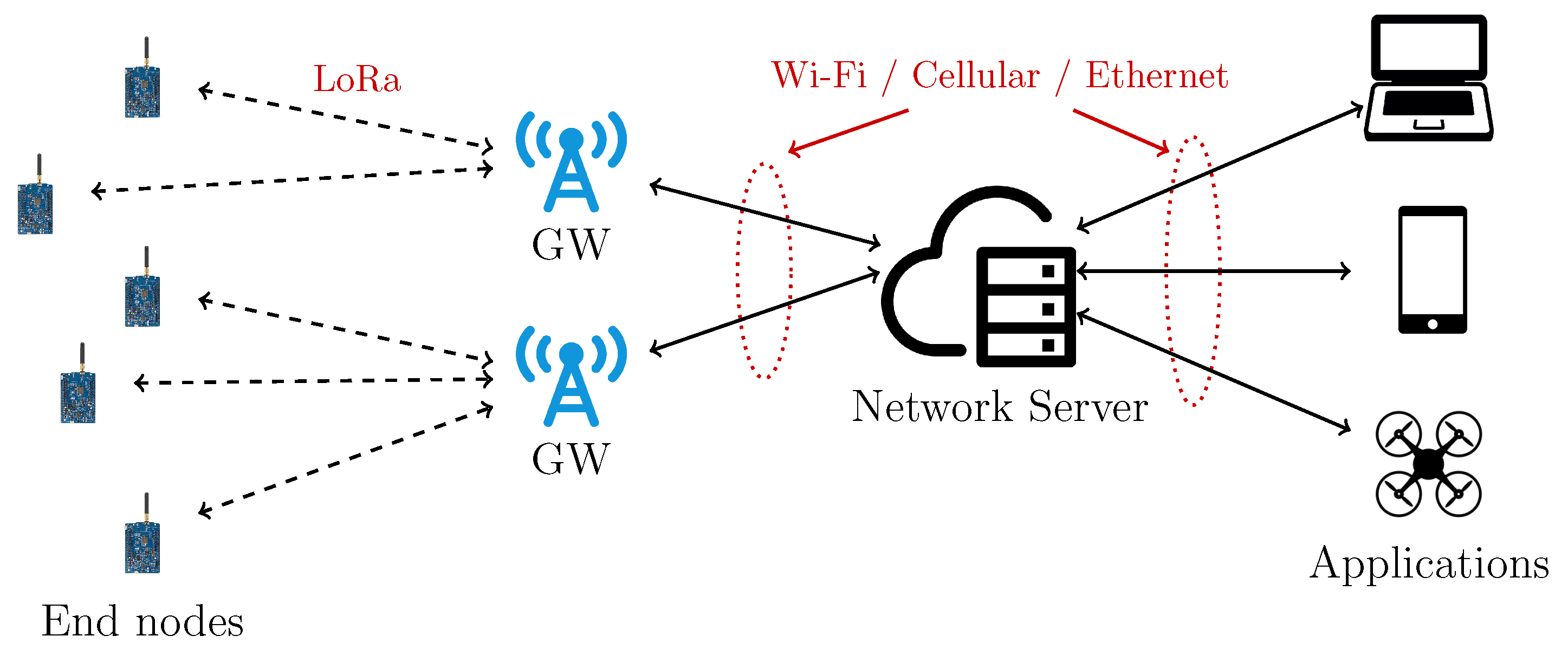
LoRaWAN network architecture [7]
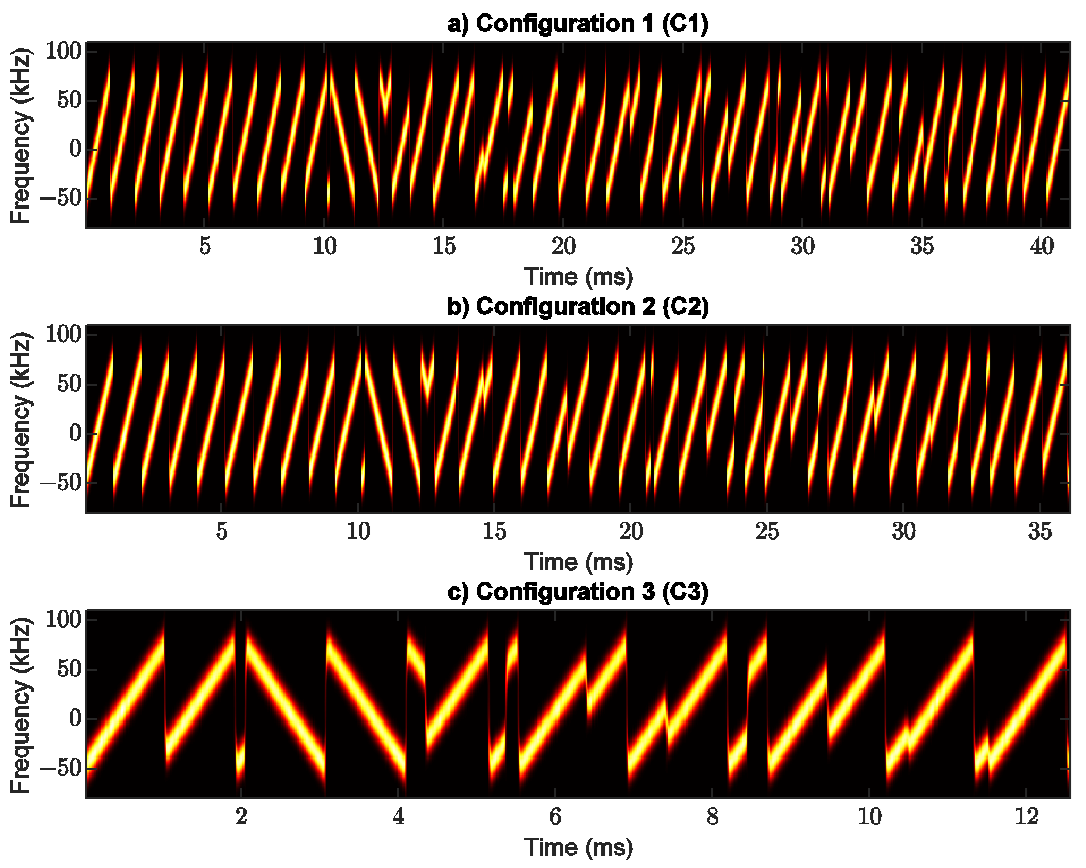
Variations on LoRa chirp characteristics [6]
References
- [1] U. Raza, P. Kulkarni and M. Sooriyabandara, "Low power wide area networks: An overview", IEEE Commun. Surveys Tuts., vol. 19, no. 2, pp. 855-873, 2017.
- [2] D. Magrin, M. Centenaro and L. Vangelista, "Performance evaluation of LoRa networks in a smart city scenario," 2017 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), Paris, France, 2017, pp. 1-7, doi: 10.1109/ICC.2017.7996384.
- [3] F. Van den Abeele, J. Haxhibeqiri, I. Moerman and J. Hoebeke, "Scalability Analysis of Large-Scale LoRaWAN Networks in ns-3," IEEE Internet of Things Journal, vol. 4, no. 6, pp. 2186-2198, Dec. 2017, doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2017.2768498.
- [4] Semtech, “SX1726 Product Details”. [Online]. Available: https://www.semtech.com/products/wireless-rf/lora-connect/sx1276
- [5] Reyax Technology, “RYLR896 Specification”. [Online]. Available: https://reyax.com/products/rylr896/
- [6] A. Gutiérrez-Gómez et al., “A Propagation Study of LoRa P2P Links for IoT Applications: The Case of Near-Surface Measurements over Semitropical Rivers,” Sensors, vol. 21, no. 20, p. 6872, Oct. 2021, doi: 10.3390/s21206872. [Online]. Available: http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/s21206872
- [7] G. Codeluppi, A. Cilfone, L. Davoli, and G. Ferrari, “LoRaFarM: A LoRaWAN-Based Smart Farming Modular IoT Architecture,” Sensors, vol. 20, no. 7, p. 2028, Apr. 2020, doi: 10.3390/s20072028. [Online]. Available: http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/s20072028
- [8] V. Talla, M. Hessar,B. Kellogg, A. Najafi, J. Smith, S. Gollakota. “LoRa Backscatter: Enabling The Vision of Ubiquitous Connectivity”. Proceedings of the ACM on Interactive, Mobile, Wearable and Ubiquitous Technologies. May 2017, doi: 10.1145/3130970. [Online]. Available: https://doi.org/10.1145/3130970