Chapter Contents
Previous
Next
|
Chapter Contents |
Previous |
Next |
| The ARIMA Procedure |
The MINimum Information Criterion (MINIC) method can tentatively identify the order of a stationary and invertible ARMA process. Note that Hannan and Rissannen (1982) proposed this method, and Box et al (1994) and Choi (1990) provide useful descriptions of the algorithm.
Given a stationary and invertible time series
![]() with mean corrected form
with mean corrected form
![]() ,
with a true autoregressive order of p,
and with a true moving-average order of q,
you can use the MINIC method to compute information criteria
(or penalty functions) for various autoregressive and moving
average orders. The following paragraphs provide a brief
description of the algorithm.
,
with a true autoregressive order of p,
and with a true moving-average order of q,
you can use the MINIC method to compute information criteria
(or penalty functions) for various autoregressive and moving
average orders. The following paragraphs provide a brief
description of the algorithm.
If the series is a stationary and invertible ARMA(p,q) process of the form
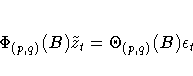
the error series can be approximated by a high-order AR process

where the parameter estimates
![]() are obtained from the Yule-Walker estimates. The choice of
the autoregressive order,
are obtained from the Yule-Walker estimates. The choice of
the autoregressive order, ![]() , is determined by
the order that minimizes the Akaike information criterion (AIC)
in the range
, is determined by
the order that minimizes the Akaike information criterion (AIC)
in the range
![]()

where

Note that Hannan and Rissannen (1982) use the Bayesian information criterion (BIC) to determine the autoregressive order used to estimate the error series. Box et al (1994) and Choi (1990) recommend the AIC.
Once the error series has been estimated
for autoregressive test order
m = pmin, ... , pmax and
for moving-average test order
j = qmin, ... , qmax,
the OLS estimates
![]() and
and ![]() are computed
from the regression model
are computed
from the regression model

From the preceding parameter estimates, the BIC is then computed

where

where ![]() .
.
A MINIC table is then constructed using BIC(m,j)
(see Table 7.5).
If ![]() , the preceding regression
may fail due to linear dependence on the estimated
error series and the mean-corrected series.
Values of BIC(m,j) that cannot be computed are set to missing.
For large autoregressive and moving average test orders
with relatively few observations, a nearly perfect fit can
result. This condition can be identified by a large
negative BIC(m,j) value.
, the preceding regression
may fail due to linear dependence on the estimated
error series and the mean-corrected series.
Values of BIC(m,j) that cannot be computed are set to missing.
For large autoregressive and moving average test orders
with relatively few observations, a nearly perfect fit can
result. This condition can be identified by a large
negative BIC(m,j) value.
| MA | ||||||
| AR | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | · | · |
| 0 | BIC(0,0) | BIC(0,1) | BIC(0,2) | BIC(0,3) | · | · |
| 1 | BIC(1,0) | BIC(1,1) | BIC(1,2) | BIC(1,3) | · | · |
| 2 | BIC(2,0) | BIC(2,1) | BIC(2,2) | BIC(2,3) | · | · |
| 3 | BIC(3,0) | BIC(3,1) | BIC(3,2) | BIC(3,3) | · | · |
| · | · | · | · | · | · | · |
| · | · | · | · | · | · | · |
|
Chapter Contents |
Previous |
Next |
Top |
Copyright © 1999 by SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA. All rights reserved.