Opening Local Files
The Analyst Application supports many different file formats,
including SAS data sets, Excel
spreadsheets, Lotus spreadsheets, SPSS portable files, and delimited
files. You can open data files from
your operating system's directories or folders and bring them into the
data table by
selecting File  Open ...
Open ...
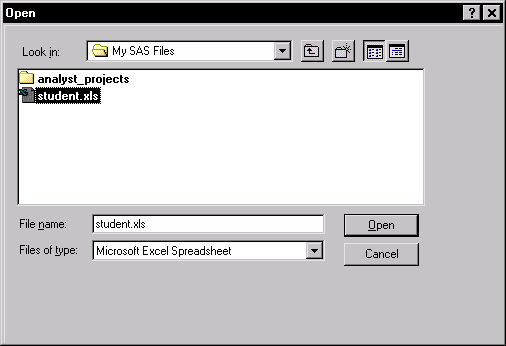
Figure 2.2: Open Dialog
In the Open dialog, select a file and click Open to bring the contents of the file
into the data table.
Non-SAS files opened into Analyst are converted into SAS data sets. The source files are
not altered.
The Analyst Application enables you to open spreadsheets from many Excel formats
including Excel 4, Excel 5, Excel 7, and Excel 97. To bring a Microsoft
Excel spreadsheet into the data table, you must ensure that rows
correspond to observations and that
columns correspond to variables. In addition, you can include variable names
in the first row of the spreadsheet.
To open a Microsoft Excel spreadsheet in Analyst, follow these steps:
- Select File
 Open ...
Open ...
- Click on the arrow next to Files of type: and select
Microsoft Excel Spreadsheet from the list.
Figure 2.3: Open Dialog with Microsoft Excel Spreadsheet Selected
- Go to the directory in which the spreadsheet is stored, select
the file, and click Open.
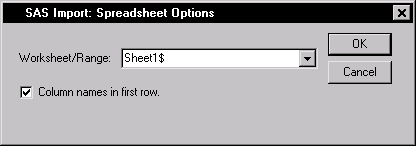
Figure 2.4: SAS Import: Spreadsheet Options Window
Figure 2.4 displays the SAS Import: Spreadsheet Options window. You
can select from a list of worksheets and named ranges. Named ranges
are predefined names that represent a range, such as a range of cells.
The Column names in first row option indicates that the first
row of the spreadsheet contains column names.
- Click on the arrow next to Worksheet/Range: and select the
worksheet or named range.
- If the first row of the spreadsheet does not contain variable
names, deselect
Column names in first row.
- Click OK to open the spreadsheet into the data table.
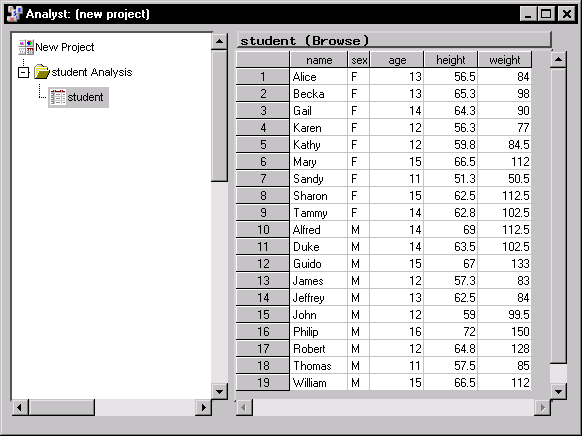
Figure 2.5: Data Table with Data from a Microsoft Excel Spreadsheet
The Analyst Application also provides access to data contained in
delimited text files. Text files typically contain variable names on
the first line and observations on following lines. Each variable
name and data value is separated by a comma, semicolon, tab, or other
delimiter. Figure 2.6 displays a text file that contains data
with values separated by commas.
Figure 2.6: Delimited File with Comma-Separated Values
To open data from a text file, follow these steps:
- Select File
 Open ...
Open ...
- Click on the arrow next to Files of type: and select
Delimited File from the list.
- Go to the directory in which the text file is stored, select the file, and click Open.
Once you have selected a text file to open, you can specify how the file is delimited
in the SAS Import: Delimited File Options window.
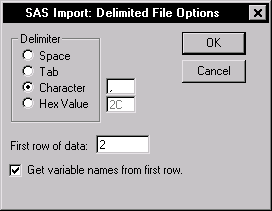
Figure 2.7: Delimited File Options Window
- Select the type of delimiter in the Delimiter box. If the
text file is not space- or tab-delimited, you can specify a custom
delimiter such as the comma, colon, or semicolon by selecting
Character and typing the delimiter in the field.
- Specify the row number that contains the first row of data. The
default row number is 2, which is appropriate for files that contain
variable names in the first row.
- Select Get variable names from first row if the first row
of the file contains variable names.
- Click OK to open the data into the data table.
To open an SPSS portable file into Analyst, follow these steps:
- Select File
 Open ...
Open ...
- Click on the arrow next to Files of type: and select
SPSS File from the list.
- Go to the directory in which the SPSS file is stored and
select the file.
- Click Open to open the data into the data table.
Copyright © 1999 by SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA. All rights reserved.
![]() Open ...
Open ...