 Introduction
Introduction
Background Information: About Korea
Geographically, Korea is a transitional zone
between the continental landmass of northeast Asia and the island arc rimming
the western Pacific Ocean. The
climate of Korea is characterized by four distinct seasons: spring, summer,
autumn and winter. The contrast between winter and summer is striking. Winter
is bitterly cold and is influenced primarily by the Siberian air mass, while
summer is hot and humid due to the maritime pacific high. The variation of annual mean
temperature ranges from 10 degrees to 16 degrees except for the mountainous
areas. August is the hottest month with the mean temperature ranging from 20
degrees to 26 degrees. January is the coldest month with the mean temperature
ranging from -5 degrees to 5 degrees. Annual precipitation is about 1,500mm in
the central region. More than a half of the total rainfall amount is
concentrated in summer, while precipitation of winter is less than 10% of the
total precipitation. The rainy season over Korea continues for a month from
late June until late July. A short period of rainfall comes in early September
when the monsoon front retreats back from the north. This rain occurs over a
period of 30-40 days in June through July at all points of South Korea. Annually, about 28 typhoons occur in
the western Pacific. Generally speaking, only two or three among them approach
the Korean Peninsula from June through September. Thus inadequate rainfalls and typhoons are
liable to cause floods and landslides.
Here are the maps
that show the location of Korea

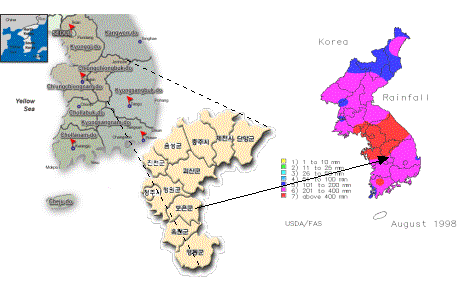 Location: Boun at Chungchongbukto has been
chosen for this particular study.
Boun is located at latitude 127 39 36 - 127 45 00 and longitude 36 25 21
– 36 30 00. Surrounded by high mountains, heavy
concentration of rainfall occurs frequently in Boun. The amount of rainfall at Boun is shown on the map
Location: Boun at Chungchongbukto has been
chosen for this particular study.
Boun is located at latitude 127 39 36 - 127 45 00 and longitude 36 25 21
– 36 30 00. Surrounded by high mountains, heavy
concentration of rainfall occurs frequently in Boun. The amount of rainfall at Boun is shown on the map
Daily rainfall: Aug
11 - Aug 12 348mm Max rainfall per hour: 92mm
Source - newspaper
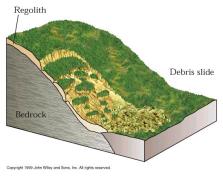 Landslides occurring at Boun include ground
movements such as rock falls, deep failure of slopes, and shallow debris flows.
Although gravity acting on an over steepened slope is the primary reason for a
landslide, there are other contributing factors causing landslide at Boun:
Landslides occurring at Boun include ground
movements such as rock falls, deep failure of slopes, and shallow debris flows.
Although gravity acting on an over steepened slope is the primary reason for a
landslide, there are other contributing factors causing landslide at Boun:
- erosion by rivers creates oversteepened slopes
- a certain type of rock and soil are weakened through
saturation by heavy rain and
strong wind
- fault creates stresses that make weak slopes fail
- excess weight from accumulation of rain may stress weak
slopes to failure and other structures
- a lower threshold of precipitation initiates landslide
(area where no tree is found)
1)
To determine
areas of susceptible location to landslide in Boun at ChungChangbukdo, Korea by
applying spatial analysis through Geographic Information Science technology
(Idrisi software)
2)
To
prevent a possible disaster (landslide) in Boun by applying Landslide
Prevention Technology on the susceptible areas
Please
click here
for Data Collection
Or click here
to go back to Index
