| Spatial Analysis |
5.2 Images Involved in Weighted Linear Combination
Before creating the fuzzy images below to be weighted with WLC, I had to create distance images for all of my factors. These distance images can be viewed by clicking on the link below each fuzzy image.
Fuzzy Images for the Five Factors Affecting Safety:
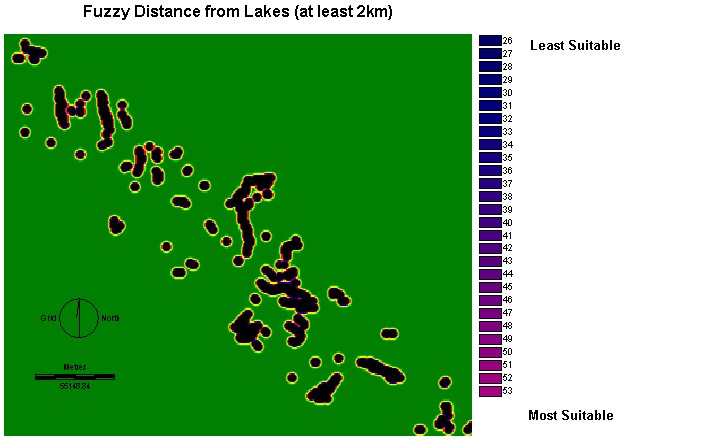
Distance Image
from lakes (LAKEDIST)
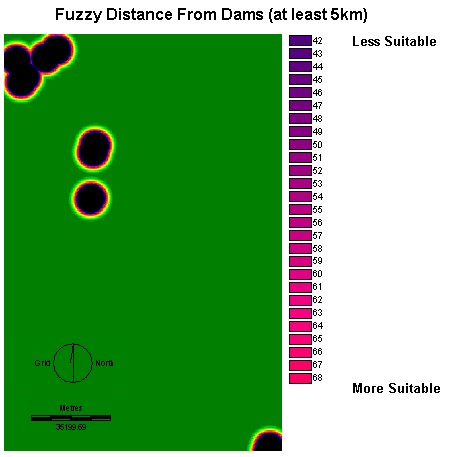
Distance Image from
dams (DAMDIST)
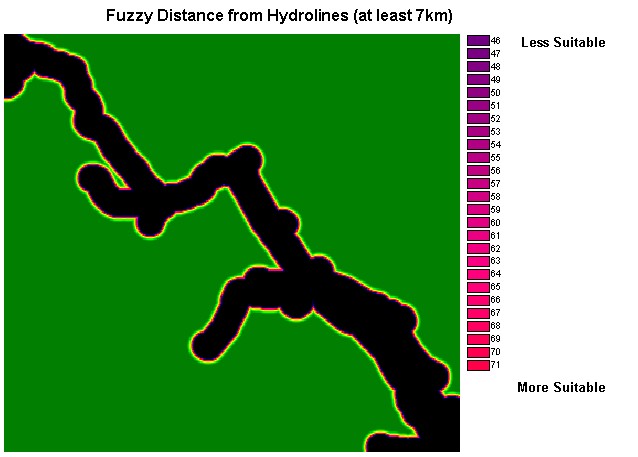
Distance Image
from hydrolines (HYDRLINEDIST)
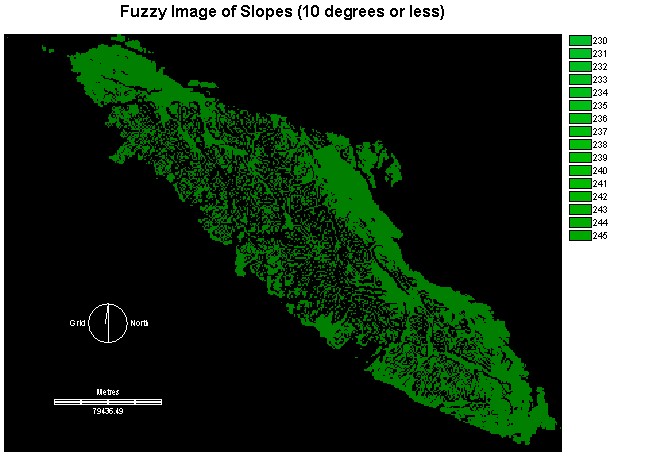
Distance Image
from slopes (SLOPEDIST)
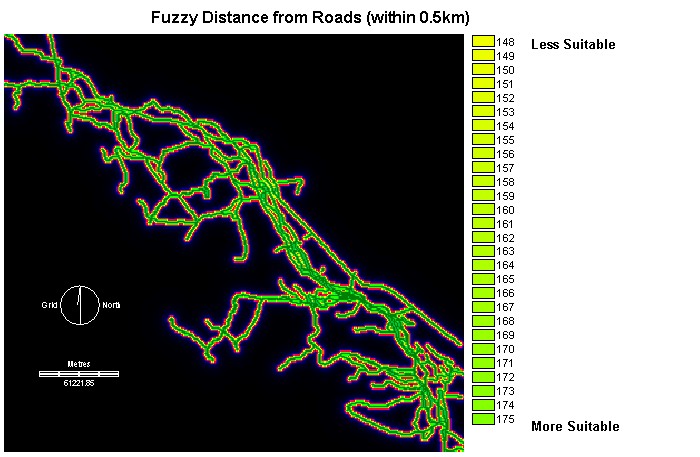

Distance Image
from roads (ALLROADSDIST)
Below is the final image produced with the Weighted Linear Combination operation. This image has taken into account the significance of the individual factors shown above. Each factor was given a specific weight by creating a pairwise comparison matrix where two factors were compared at once until all possible combinations of two factors had been made and weights had been assigned. Generally speaking, the order I considered the factors with regards to importance from greatest to least was hydrolines, dams, slopes, lakes and roads. To see the specific weight applied to each factor see specific weights.
The areas on the image below whose colour correspond with the shade of green represented by the value of 255 in the legend indicate the safest places to live on Vancouver Island in an earthquake given the particular criteria that I have analyzed. Areas represented by black indicate the most dangerous locations on the island in the event of an earthquake. These areas are in close proximity to hydrolines and dams which were weighted as having a heavy significance in my WLC analysis.
RESULTS- Comparison of Boolean MCE and WLC methods of analysis:
Overall I found the WLC method to provide much more accurate results as to where the safest location to live on Vancouver Island is during an Earthquake. The reason why this method is better is because it takes into account a real-life situation which involves factors of varying importance. Using the WLC method allows you to apply weights to the individual factors accordingly with their significance in terms of how much damage they may cause during an earthquake. Obviously being near a hydroline will have severe implications and should therefore be weighted heavily. Living nearby to a road is a benefit during an earthquake because it allows for faster evacuation, however it is not a life-threatening issue and should therefore not be weighted as heavily as distance from hydrolines.
As you can see by comparing the two final images, that from the Boolean
MCE operation and the WLC operation, the Boolean operation simply defines
areas as being suitable or unsuitable. The WLC operation on the other
hand illustrates the degree of suitability of different areas by giving
each area a value from 0 (completely unsuitable and unsafe) to 255 (the
safest overall area). If I had to rely on one of these methods to
determine where to locate on Vancouver Island, keeping in mind the potential
for a future earthquake, I would definitely choose the WLC method of weighting
factors to determine the best place.
![]() Boolean Multi-Criteria Evaluation
Boolean Multi-Criteria Evaluation
![]() Methodological and Operational Problems
Methodological and Operational Problems