|
The
District of North Vancouver
|
Spatial
Analysis
Boolean
Multicriteria Evaluation
The following two images are images that have
been zoomed in order to depict a detailed image of the area under discussion.
ZONING Map of DNV
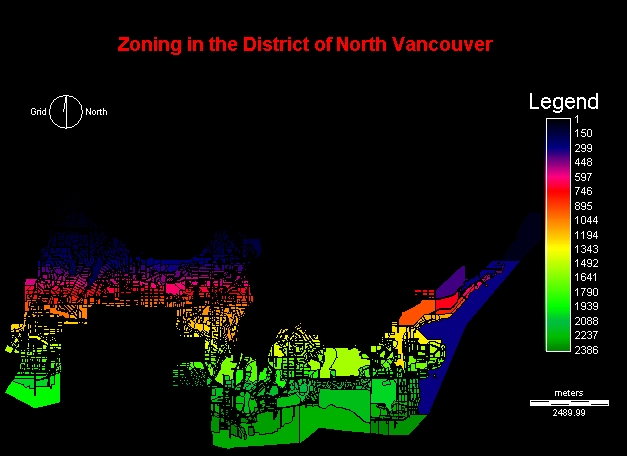
This is the map that was used as a base map for
all the further analysis.
From this image I was able to create an image
of all areas that are available for development. I then rasterized
that layer and called it DEVELOPMENT.
Constraints
DEVELOPRAS Map of DNV
This map represents all the possible areas for
development, but from these areas the best potential sites must be located.
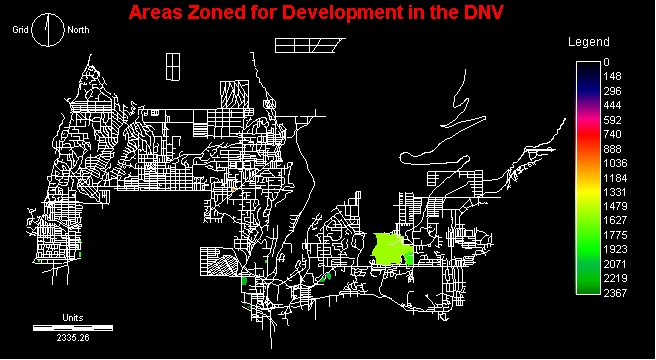
It is difficult to see some of
the smaller areas for potential development to the far left.
See
Cartographic Model
Distance Images
These images show the distance from creeks and industrial areas.
The distances can be reclassified into Boolean images depicting suitable
and unsuitale areas for housing development.
Boolean Images created from the distances
Factors
Both distances from elementary schools and parks were considered factors
in the analysis as it is preferable to have both nearby, yet they don't
completely restrict development from occuring in any way.
Boolean Images
As can be noted in the images above, most areas in the DNV lie within 500m
of parks and elementary schools are well spread out over much of the region.
However, despite these factors, development is constrained within development
zones that meet these criteria.
In an attempt to illustrate adjacency, I produced a frictional surface
of DEVELOPRAS and used
it within the cost distance analysis of MULTIRESRAS

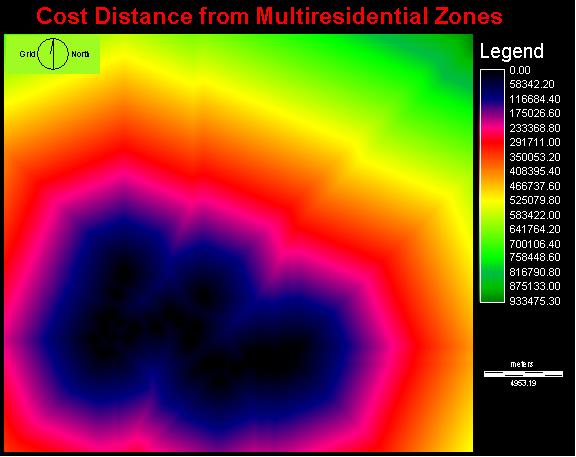
Boolean Multi-Criteria Evaluation
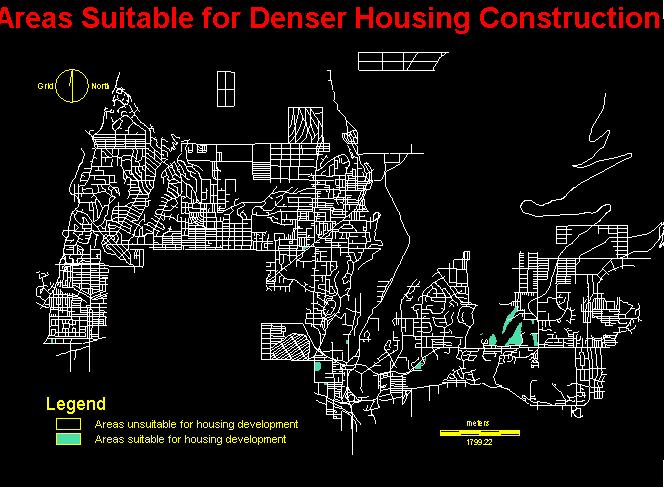
See cartographic Model
This image
shows the various areas that are possible locations for housing development.
As we can see, the main area on the right is crossed by creeks that prohibit
development from those area. It is however, impossible to know from the
image whether these creeks are actually above ground or not. That
would be interesting infomration to have included within the database.
 Weighted
Linear Combination
Weighted
Linear Combination
 Back
to Table of Contents
Back
to Table of Contents