![]()
Thus use of the two sample t based confidence interval
(on 33 degrees of freedom) gives the interval
![]() or -0.19 to 5.29. Using the interval which does not pool seems inadvisable
here since one of the two sample sizes is small. However, the unpooled
estimated standard error of the difference in means is
or -0.19 to 5.29. Using the interval which does not pool seems inadvisable
here since one of the two sample sizes is small. However, the unpooled
estimated standard error of the difference in means is
![]()
Thus this interval, using the normal multiplier 1.96 is -0.1 to 5.2. (Aside: there is an approximation due to Welch or Satterthwaite to the distribution of the t-statistic which leads to using the large sample statistic but with a t multiplier with degrees of freedom being
![]()
where

which comes to 20.16 degrees of freedom leading to the multiplier
2.085 and the interval ![]() which runs from
-0.22 to 5.32.)
which runs from
-0.22 to 5.32.)
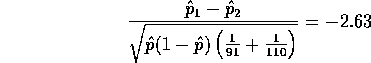
leading to a P-value of 0.85% which is strong evidence against equal probabilities.
![]()
or ![]() . The subscript 1 refers to foreign drivers.
. The subscript 1 refers to foreign drivers.
- A standard two sample problem with 2 independent samples.
The z statistic is

Since the sample sizes are equal the pooled and unpooled versions are identical. The statistic works out to -6.4 which is overwhelming evidence that the two filling operations produce different mean weights.
- This is a one sample problem testing
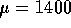 against
the alternative that it is more than 1400. The
statistic is
against
the alternative that it is more than 1400. The
statistic is
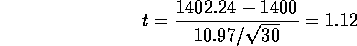
yielding a one sided P-value of 13.6% from a t distribution on 29 degrees of freedom or of 13.1% from the normal curve showing that it doesn't really matter which you use. This is only very weak evidence against the null hypothesis which wold be accepted.
| First 20 | Second 20 | Difference |
| 850 | 890 | -40 |
| 740 | 840 | -100 |
| 900 | 780 | 120 |
| 1070 | 810 | 260 |
| 930 | 760 | 170 |
| 850 | 810 | 40 |
| 950 | 790 | 160 |
| 980 | 810 | 170 |
| 980 | 820 | 160 |
| 880 | 850 | 30 |
| 1000 | 870 | 130 |
| 980 | 870 | 110 |
| 930 | 810 | 120 |
| 650 | 740 | -90 |
| 760 | 810 | -50 |
| 810 | 940 | -130 |
| 1000 | 950 | 50 |
| 1000 | 800 | 200 |
| 960 | 810 | 150 |
| 960 | 870 | 90 |
| Average=909 | Average=831.5 | Average=77.5 |
| SD=104.9 | SD=54.2 | SD=109.8 |
Has the bias of the measurements changed between the first 20 and the last 20?
Solution
This is not a paired data problem; I just calculated the differences to
confuse. There is no natural pairing between the first measurement and
the first of the last 20. Taking the two independent samples model the
question is whether the mean ![]() of the first 20 is the same as the
mean
of the first 20 is the same as the
mean ![]() of the last 20. The idea is that each mean is the true speed
of light plus a bias and so the means are equal if and only if the biases
are the same.
of the last 20. The idea is that each mean is the true speed
of light plus a bias and so the means are equal if and only if the biases
are the same.
It is not obvious that the standard deviations are unchanged (and the statistical evidence is that the standard deviation has indeed changed). We thus do not pool the estimates of the standard deviations and our test statistic is
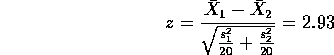
(Numerically, though, since the two sample sizes are the same the statistic has the same value as the two sample t statistic using a pooled variance estimate.) Looking in normal tables and carrying out a 2 tailed test we get a P value of 0.3% and conclude that the bias has indeed changed.
Although the data are not paired the paired comparisons t-test is still valid and the resulting statistic is 3.16 on 19 degrees of freedom yielding a P-value of 0.5% which leads to the same conclusion. The previous calculation based on the unpaired method would have had 38 degrees of freedom if the assumption of equal variances were valid and an indistinguishable P-value.
| Year | Number of | Year | Number of |
| deaths | deaths | ||
| 1875 | 3 | 1885 | 5 |
| 1876 | 5 | 1886 | 11 |
| 1877 | 7 | 1887 | 15 |
| 1070 | 9 | 1888 | 6 |
| 1879 | 10 | 1889 | 11 |
| 1880 | 18 | 1890 | 17 |
| 1881 | 6 | 1891 | 12 |
| 1882 | 14 | 1892 | 15 |
| 1883 | 11 | 1893 | 8 |
| 1884 | 9 | 1894 | 4 |
| Total | 92 | 104 |
- Use a Poisson model and obtain a 95% confidence
interval for the long run average mean number of
deaths per year.
I did this in class and obtained two intervals: the first, for the parameter
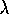 (which is the annual rate) is
(which is the annual rate) is

and the second is the interval for
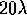 based on solving a quadratic
based on solving a quadratic
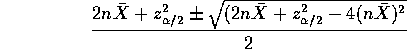
This last interval translates to one for
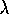 by dividing by n=20 to get
by dividing by n=20 to get
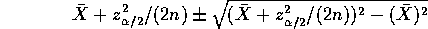
or

which is about the same width but centred slightly differently. The difference is negligible.
- Develop a test of the hypothesis that there has been
no change in this underlying death rate over the time
period in question as follows. Let N be the number
of deaths in the first 10 years and M the number in
the second 10 years. If the Poisson model with
constant death rate is credible then M and N have the
same mean. What is the standard error of N-M in
terms of the Poisson parameter? How can you estimate
this standard error? How can you use this to test
the hypothesis that there is no change in mean?
If
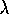 is the per year rate and this is the same for all 20 years
then both N and M have Poisson distributions with parameters
is the per year rate and this is the same for all 20 years
then both N and M have Poisson distributions with parameters
 . Then
. Then  and the
natural test statistic is
and the
natural test statistic is
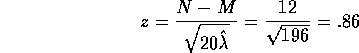
leading to a (two sided) P-value of 39% which is not significant.