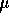 be the population mean. Then
be the population mean. Then
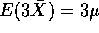 so we must evaluate
so we must evaluate 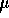 . The definition
is
. The definition
is
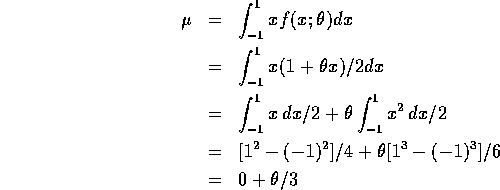
so that 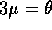 .
.
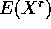 which is given
by
which is given
by
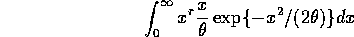
Make the substitution 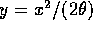 for which
for which 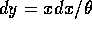 and get
and get
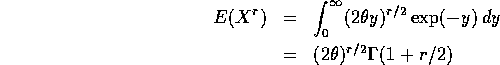
For the special case r=2 we get the formula in the book (using
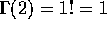 ).
).
- According to the fact
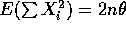 so that
so that
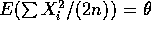 . Thus
. Thus 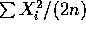 is unbiased.
is unbiased.
- You square these numbers, add then divide by 20 and get 74.505 as
in the appendix.
- The log of the density is
 so that the log likelihood is
so that the log likelihood is
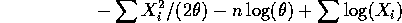
To maximize this we take the derivative with respect to
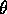 and
set the result equal to 0 getting
and
set the result equal to 0 getting

which has root
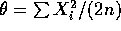 which is the same as
the unbiased estimate above.
which is the same as
the unbiased estimate above.
- The median, m, of the distribution satisfies
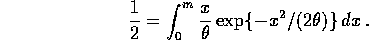
The integral may be done by substituting
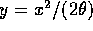 to get
to get
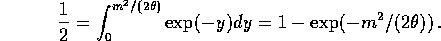
Solve this to get
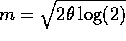 and then the mle of m
is
and then the mle of m
is
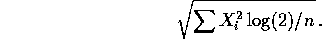
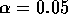 so that the
test rejects when t exceeds the t critical value on 7 degrees
of freedom. The nearest curve in Table A.13 is for 6 degrees of
freedom and the quantity d is
so that the
test rejects when t exceeds the t critical value on 7 degrees
of freedom. The nearest curve in Table A.13 is for 6 degrees of
freedom and the quantity d is 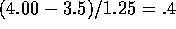 For 6 df this appears to correspond to a
For 6 df this appears to correspond to a  of around 0.76
while for 9 df we would get about 0.65. My estimate is about a third
of the way between them (because 7 is a third of the way between
6 and 9) or roughly .72.
of around 0.76
while for 9 df we would get about 0.65. My estimate is about a third
of the way between them (because 7 is a third of the way between
6 and 9) or roughly .72.
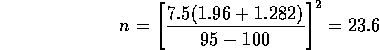
so that n=24 would be needed. Notice that the formula for the sample
size for a two sided level  test is just the same as that\
for a one sided level
test is just the same as that\
for a one sided level 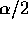 test.
test.
It is also acceptable to do this using the t-test graphs as in the previous question. In fact, I think this is what the text intended really. If so you get a sample size of 19.
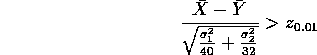
which can be rewritten as
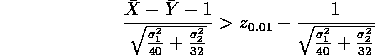
The power function at 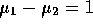 is then the area to the
right of the right hand side of this last formula under a standard
normal curve. Plugging in numbers shows that we want the area
to the left of
is then the area to the
right of the right hand side of this last formula under a standard
normal curve. Plugging in numbers shows that we want the area
to the left of 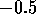 which is .31. That is
which is .31. That is  approximately.
To get a probability of type II error equal to 0.1 we need
approximately.
To get a probability of type II error equal to 0.1 we need
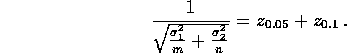
Putting m=40 and plugging all the other numbers we get
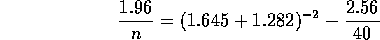
which leads to n of roughly 37 (actually a bit over so rounding up to 38 would be normal).
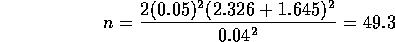
which we round up to 50 for safety's sake.