 |
The Grand Forks aquifer is situated in south-central British Columbia. Groundwater is used for domestic and municipal supply and irrigation. The aquifer consists of layered alluvial sediments overlying bedrock. The bedrock forms the lateral and lower boundary to the aquifer. The top surface of the aquifer is generally flat. The Kettle River flows from west to east through the valley and is in close hydraulic connection to the aquifer. |
|
| A digital elevation model for the bedrock surface was constructed using bedrock topography and bedrock contacts recorded in a few water wells. A regional digital elevation model (DEM) was used to extrapolate the bedrock surface beneath the surficial cover. A series of bedrock cross-sections were constructed through the valley, which were then interpolated to create a bedrock topography map. | 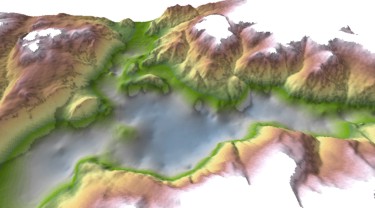 | |
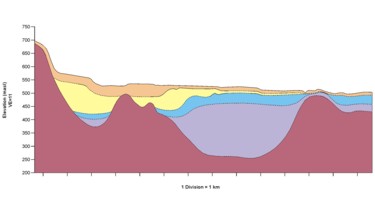 | Control wells, or wells that were deemed to have reliable records, were used to constrain the interpolation of the unconsolidated lithologic units and to create geologic cross-sections. The standardized water well lithology database was then used to infill the cross-sections so as to create a more dense coverage. | |
| Aquifer Architecture Layer contacts at each well location were interpolated between wells using the visualization software package, GMS, and were used interpolated in three dimensions using appropriate geostatistical methods. The cross-sections were interpolated to generate layers, thus providing the three-dimensional architecture for the aquifer. Ultimately, the architecture is used as input into numerical groundwater flow and transport models. | 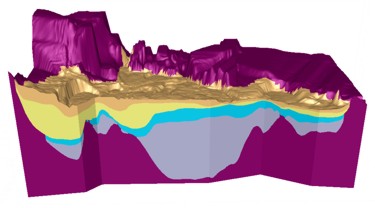 | |