Cell Cookie
Cell Cookie
A) Objective: To learn about the basic form and function of plant and animal cells and their organelles.
B) Time: 20 minutes
C) Materials:
- List materials:
- round or rectangular, 9 inch pan of rice krispie "squares" (uncut) -- 1 inch high
- thin licorice, graham wafers, jube jubes, fancy cookies, almost any assortment of junk food will do!
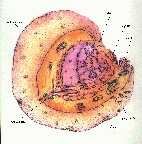
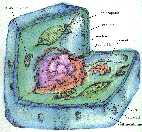
- GOOD picture of a cell and explanations of the organelles
- Materials found at:
- call up manufacturers to see if you can get the food donated (candy can be expensive). Otherwise, bulk food is a good place to try
- cell pictures can be found in any first year or high school biology text book
- Cost per camper: $1
C) Theory: Cells work like small versions of factories, or along with our Mission Impossible theme, a secret service agency building.
- Nucleus: Control center for the cell -- where all the top officials plot and plan the missons. Also contains the DNA for cell reproduction.
- Plasma Membrane: Like your skin, the plasma membrane keeps all the organelles in the cell. It lets some things, like water and ions across, but keeps outher stuff out.
- Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER): Makes stuff (products) for the cell.
- Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER): has ribosomes on it
- Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (SER): has no ribosomes on it
- Ribosomes: Site of protein construction.
- Golgi Complex/Apparatus: Modifies and packages ER products and produces vesicles.
- Vesicles: Transports products of ER -- like transport trucks.
- Peroxisome: Contains enzymes which dissolve proteins. Like your stomach -- these digest!
- Lysosomes: Gacbage Crew. Clean up damaged or dead components.
- Vacuoles: Contain water to provide firmness to cell.
- Mitochondria: Provide energy for the cell. Have their own DNA.
- Microtubules: Provide internal structure, like your bones.
- Microfilaments: Little microtubules.
Centrioles: make up the flagella and cilia.
Only in plant cells
Chloroplasts: convert sunlight into energy for plant cells. Contain chlorophyll.
Plasmodesmata: holes in the cell walls. Junctions between plant cells allowing water and ions to pass between cells.
Cell Wall: strong support, like thick concrete walls for plant cells.
E) Procedure:
- Each group of 4 gets a rice krispie square and an assortment of candy, as well as the cell picture. Round krispies are animal cells and rectangular krispies are plant cells.
- The group puts together a "cell" using the candy as organelles.
- Before the group can eat it, they must each explain each aspect of the cell and what the organelle does! As they tear it apart, they will be able to see the "microtubules" that were holding the cell together!
F) Safety: Watch for allergies -- especially nut allergies.
G) Real Life Examples: Cells, the "building blocks of life," make up all living things. Understanding their form and the function of organelles leads to a better understanding of plants and animals.