IDRISI Kilimanjaro
Step 1 : Import Data
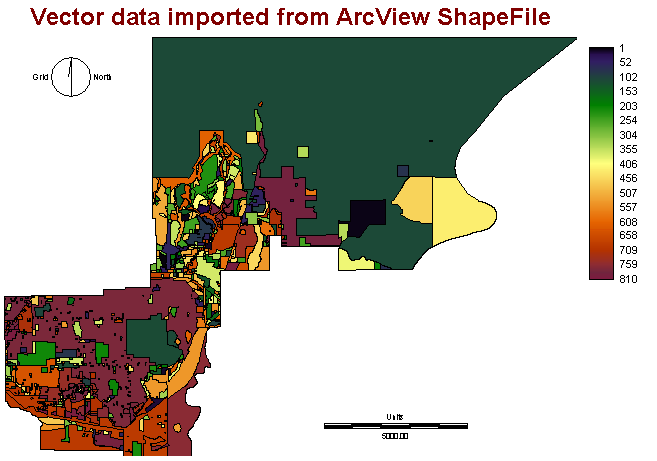
It is not easy to find IDRISI format data. However, all GIS files are inter-convertable. Data was collected from City of Coquitlam and it is under ArcView shape files format. To import data in IDRISI, i have to use the convert function, "SHAPEIDR", to process. SHAPEIDR allows user to either convert shape files to IDRISI or vice versa. In below, figure 1 and 2 show the ArcView Vector files, and Converted IDRISI Vector files.

Figure 1 IDRISI format (Vector) after convertion
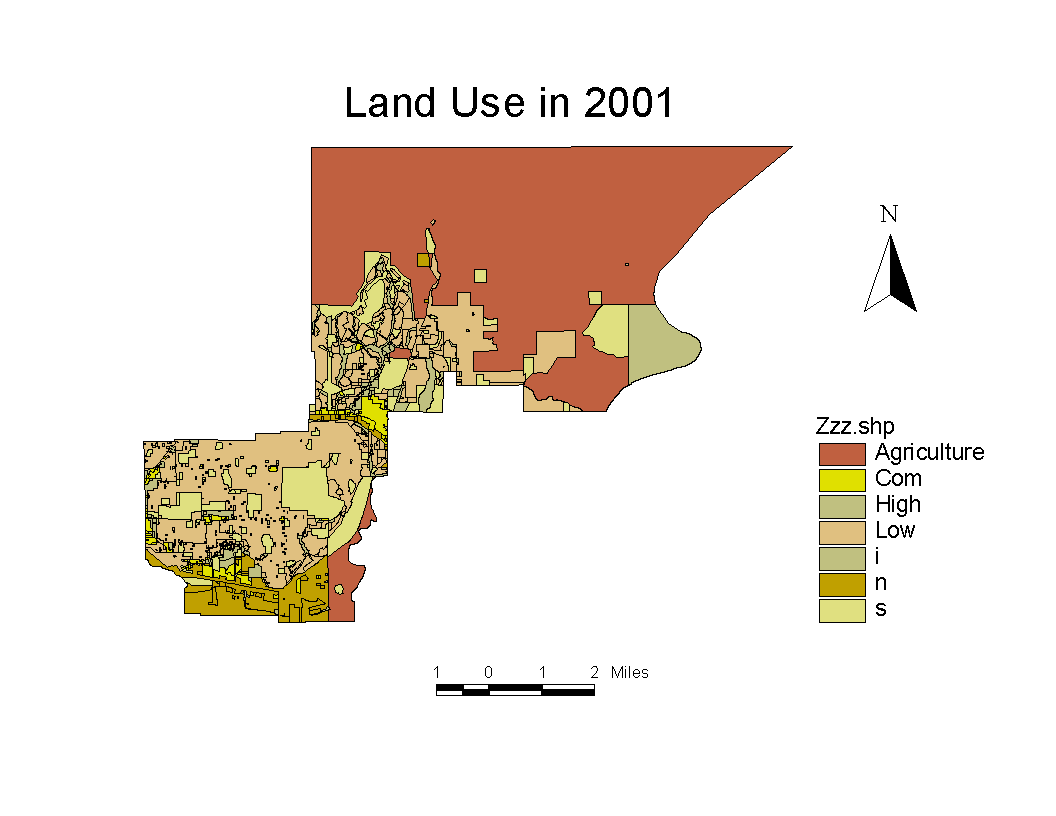
Figure 2 ArcView Shapefiles
Step 2: Reclassification + Rasterization
After the import of data, we have a vector files in IDRISI, however, the parcel is not defined in correct values. We have to use the reclassification to reclass all polygon values. It has 810 polygons in total, so we have to reclass all of them into a correct sequence. However, an error occured during the use of reclassification. Further explanation will fully discourse in Error section.
The first reclassification was only assign the new value into each polygon. We have to do the second reclassification in order to classify the parcel into land use type. For example, cell 1 to cell 5 are Agricultural land use and we assign a new value 1 to all Agricultural land. We have to input the numeric values either in "reclass table" or edit module. numbers written as 1 1 6. When we finished all reclassification and we have the nice map with land use classification. We are ready to transform into raster.
To have a future prediction on a place, a spatial decision module CA_MARKOV is the most suitable one in IDRISI. By using cellular Automata model, IDRISI can generate a future prediction based on the input layers, must have at least 2 different years, to create the probability matrix and use it to interpolate the growing. Since Cellular Automata need a raster format, we have to convert files, which import from ArcView, into a raster files.
RASTERVEC is a module that we use for convert data from Vector to Raster.
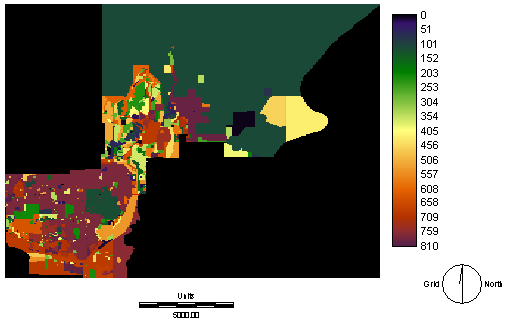
Figure 3 Raster Version of Land use
Step 3: Spatial Decision Model - MCE
MCE, Multi-Criteria-Evaluation, is a spatial decision model which generated a suitability map. It is an essential part in doign CA_MARKOV. Cellular Automata requires all suitabilities map to calculate the probabiltiy matrix.
By using Decision Wizard, we can generate the MCE image, suitability map. We also need to define the constraint and factors in order to create the image. Since i cannot reclass the model, I am not able to create an image for Coquitlam. See Error
Constraint:
Water body
Institutional land
Factors:
Within 0.5 miles to existing high density residential
within 2 miles of commerical area
Module may also need user to create distance map and fuzzy map in Decision Wizard. These are necessary because it determines which area are suitable for growing.
At last, user has to weight the importance of land use. It is necessary to have a proper weighting because it indicates the importance of each layer, so system can determine the result.
When we finished producing a group of suitability map, we group it into a single folder than using command "MARKOV" to create probability matrix and condition probability image. These tables and images are essential because CA_MARKOV module require these in order to perform the result. Furthermore, we have to set a time range for our model. For example, if i am interested what will be the growth in 20 years later, then i have to set the time range as 20 years. So that the module can calculate for you.
Unfortunately, I cannot post any images because error was taken place during working on data editing. All steps that provided above were based on what i plan to do in my project.